Lecture 2
advertisement

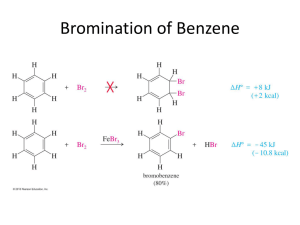
[Year] ORGANIC II TEAM Lecture 2 Clinical Pharmacy Cairo University 2014/2015 /Clinical2020CU Organic Chemistry II Lecture 2. Let’s begin with some questions on lecture 1 to refresh our minds ;) Which of the following compounds is aromatic, anti-aromatic & non-aromatic and why: 1. C7H8. Non-aromatic, as not all carbons are SP2. 2. C7H7 + Aromatic, all carbons are SP2, obeys Huckle’s rule πe’s = 6. 3. C7H7 – Anti-aromatic, doesn’t obey Huckle’s rule πe’s = 8. Complete the following table: Reactions Reagent used Nitration Sulphonation Electrophile** Conc. HNO3/H2SO4 1 SO3/ H2SO4 Sulphur trioxide SO3 3 Br2 or Cl2 in Cl2 or Br2 -lewis presence of lewis acid complex. acid. Alkylation 4 Alkyl halide- AlCl3 complex. Acylation Acyl halide in 5 presence of lewis acid. 1- NO2 + Nitronium ion. 2- Benzene sulphonic acid. 3- Halogenation. 4- Alkyl halide/ AlCl3. 5- Acylium ion “stable compound” CH3 – C Ξ O+ Clinical 2020 Product of reaction Nitrobenzene. 2 Chlorobenzene or Bromobenzene. Alkylbenzene. Acylbenzene (aryl ketone). Halogenation of benzene WE WILL START BY MECHANISM OF BROMINATION: “similar to chlorination” STEP 1: Formation of electrophile from reagent: Br2- lewis acid complex E+ فبقىBr فبكدا عدد االلكترونات قل من على الFeBr2 معbond عملتBr إيه بقى اللي حصل؟! االكترونات بتاعت .+ve charge عليها شحنة موجبة STEP 2: Addition of electrophile E+ : الهجوم دايما من.Br بتاعت البنزين هتاخدelectron cloud وattraction عليها شحنة موجبة هيحصلBr بما إن علشان تكونFeBr3 دخلت على البنزين والتانية فضلت معBr اللي حصل إن واحدة من...سالب لموجب مش العكس .Deprotonation ودي ليها دور مهم جدا في الخطوة الجايةFeBr4Step 3: Deprotonation of intermediate carbocation by base to regenerate aromaticity: . طلع زي ما دخلFeBr3 وH آخر خطوة بنشيل :Halogenation خمس نقاط مهمة في .bromination للmechanism له نفس الChlorination ناشط جدا ال يمكن السيطرة عليه ودي مشكلة ألنه مش بيطلعfluorine مش بيتعمل؛ بسبب إنFluorination .الناتج المطلوب Clinical 2020 Iodination بطئ جدا ليه؟؟ علشان هو مش ناشط للبنزين بس ناشط لما يتفاعل مع بنزين ناشط..يعني إيه؟ بمعنى إن البنزين ده مع groupبتنشط البنزين حيث إنها تمتلك +M effectاللي بيزود الكترونات π bondفيساعد التفاعل زي Phenolيقدر يتفاعل مع .I2 Phenols & Aniline دول ناشطين جدا مع halogenبدون مساعدة Lewis acidنظرا إن OH, NH2عندهم +M effectوده هيزود كثافة االلكترونات في البنزين فتقدر تخلي Br2 & Cl2يبقوا .polarized ليه بنستخدم Lewis acid؟؟ علشان يخلي Br2 & Cl2يبقوا ،polarizedألن البنزين ما يقدرش يعمل كدة علشان هو مستقر جدا و electrons πمحكمين “benzene π electrons are tightly held & aren’t able to polarize alone”. Friedel Craft Alkylation Benzene + alkyl halide in presence of AlCl3 to give alkylbenzene. الجزء ده محتاج تركيز ...في حالة alkylationاحنا اتفقنا إن ال reagentكان إيه ؟؟ بالظبط إنت برنس ( (Yال reagentكان ... Alkyl halide/AlCl3جميييل جمييييل *على طريقة ناصر في :D *arabs’ got talent Alkyl halide can be 2ry or 3ry Alkyl halide )(Free carbocation, most stable Clراحت مع AlCl3وكونت .AlCl4- AlCl3هتطلع في اآلخر زي ما دخلت. Primary Alkyl halide ”“CH3 CH2Br AlCl3 ) (CH3 CH2-Br+ - AlCl3- ال chargesدي بقى جت منييين؟ ركز معايا، ال Alده metalهيسحب الكترونات من Br وتكون عليه –ve chargeأما Brيبقبى عليه +ve ألنه فقد e’sودي مش مشكلة ألنه هيسحب e’sمن CH3CH2 وتكون +veويبقى هو الelectrophile Clinical 2020 1ry Alkyl Halide Mechanism: Step 1: ال +veعلى Brبتتعوض من Alkylألن Brعندها –Iهتسحب و +M alkylهتدي الكترونات. Step 2: ال electron cloudهتهجم على Alkylبما إن الهجوم من سالب لموجب **لو عكست السهم هتبقى غلط ركززز** (– (Brهتشيل ال Hفي خطوة ال.deprotonation Step 3: AlCl3هيطلع زي ما هو ،وال Hهتتشال واالكترونات هتعمل double bondتاني. ونفس الكالم بالنسبة لخطوات ال .3ry Alkyl halide Clinical 2020 NO2 زيstrong deactivating group مش هيحصل في البنزين لو ماسكةFriedel Craft’s reaction فكدة أقدرstrong deactivating تعتبرNO2 ألن، مش هينفاعل في التفاعل دهnitrobenzene ده معناه إن .reaction علشان هو مش هيتفاعل فمش هيأثر في الsolventاستخدمه كـ Benzene هيتم بنجاح معFriedel Craft’s reaction Benzene activated with activating group (-R, -OR, -NHCOR) Halobenzene **Activating & deactivated will be explained later** Benzene with NH2 , NHR, NR2 & OH do not undergo Friedel Craft’s Alkylation. Explain. Because unshared electrons nitrogen form a complex with AlCl3 which is electron withdrawing group so deactivate the ring (carry +ve charge). دهcomplex و الAlCl3 معcomplex هتعملlone pair يعني إيه الكالم ده؟؟ يعني علشان نيتروجين عندها يبقى عليهcomplex والdeactivated يعني بيسحب الكترونات ويخلي البنزينelectron withdrawing .+ve Clinical 2020 في عوامل بتحد من التفاعل ده **ركز معايا** : Aryl halide -1أو vinyl halideمش هيعملوا carbocationبسهولة فبالتالي هما .unreactive Polyalkylation -2يعني إيه؟؟ poly = manyبمعنى إن هيحصل كذا Alkylationوعشان Alkyl بتنشط البنزين وبتوجه ال other alkylsفي .ortho,para positionبردو هتتشرح قدام وعلشان نتغلب عليها ممكن نزود عدد aromatic compoundليه؟؟ علشان لما يكونوا كتير خصوصا أكتر من alkylكل alkylهتتفاعل مع بنزين فمش هيحصل polyalkylationنظرا إن عدد البنزين أكتر من .Alkyl group سؤال ممكن ييجي في الشفوي ما هي عيوب ال Alkylation؟ Polyalkylation .1لما آجي أدخل CH3على .benzene زي ما اتشرح فوق وقولنا أعالج المشكلة دي إزاي. Rearrangement .2 ألن ممكن Alkylيبقى primaryوده less stableفيحصله إعادة ترتيب عشان يبقى secondary or tertiaryودول ...more stableوده يعتبر عيب ألن الناتج مش بيبقى .pure Nitrobenzene & Aniline can’t react by alkylation .3 NO2فى ال nitrobenzeneدي deactivatingفمش هيحصل .Alkylation NH2في ال Anilineدي activatingبس لما بيحصل complexمع AlCl3ال complexده فيه حاجتين: .Iهيبقى electron withdrawingهيسحب االلكترونات ويحصل خلل. Complex carries charge .IIوده هيزود الخلل ...بالتالي الناتج مش هيبقى مستقر. Clinical 2020 Friedel Craft’s Acylation Electrophile used: Acylium ion CH3 – C Ξ O+ Step 1: Formation of E+ : .إيه ده اللي حصل ده !!! ركز معايا كدة (R-C+=O ( وتسيبAlCl4- عشان ت َكونAlCl3 – وهتروح للI عشان عندهاcarbonyl group هتسحب الكترونات منCl +ve عليهاO وال4 bonds هيبقى عندهاC فكداC معbond هيعملواOxygen منlone pairواللي هيحصل إن ال .electrophile ( هوR-C+=O( وكدة ال Step 2: Benzene reacts with E+ : Step 3: Clinical 2020 Step 4: وي ًكونe’s هيسحبmetal دهAl والlone pair ( عليهاO) ،الفكرة دي اتقالت قبل كدة...AlCl3 هيحصل تفاعل تاني مع Ketone- Aluminium chloride complex" وله اسم تانيcomplex . لوحدهketone هيطلعhydrolysis دهComplex لو عمالنا لل : له مميزاتAlkylation عكسAcylation كانتalkyl على عكسdeactivating بتعملAcyl group (R-C+=O) بس ليه؟؟ علشانNo polyacylation -1 .activation بتعمل وده يخلي البنزين تعملe’s بتسحبcarbonyl C=O علشان.. ؟ سؤال ممتازdeactivating طب ليه بتعمل .activating فبتعملe’s كانت بتديAlkyl لكنdeacativating Clinical 2020 carbocation بيتنقل في شكلAlkyl ألنها بتتنقل بدون أي شحنة على عكسNo rearrangement occurs -2 .more stable بيتعاد ترتيبه علشان يبقىprimay alkyl ولو طب إزاااي؟،alkylation أعالج إعادة الترتيب اللي بتحصل في الacylation ممكن عن طريق تفاعل ال-3 alkyl هيطلعreduction بعدها أعملacyl benzene فيطلعacylation عن طريق إنك تعمل للبنزين .rearrangement ومش محتاج أعملbenzene Reactivity & Orientation in electrophilic aromatic substitution When substituted benzene undergoes electrophilic substitution, substituent group already present affect: 1- Reactivity. 2- Orientation وده بيعتمد على، وسرعة التفاعلsecond substitution بيتحكم في مكانfirst substitution بمعنى إن inductive & mesomeric effects. :يال نفتكرهم مع بعض بسرعة Inductive effect: is displacement of electrons towords highest electron negativity on sigma bond. مجرد إزاحة االلكترونات في اتجاه الذرة عالية السالبية It has 2 types: +I donating electrons (releasing). -I withdrawing electrons. Mesomeric: is redistribution of electrons on pi bond.إعادة ترتيب االلكترونات Its 2 types: +M releasing e’s. -M withdrawing e’s. Clinical 2020 X is the first substituent, Other arrows are second substituents. X determines position of second substituent & rate of reation. .+I or –I or +M or –M ديX وده بيعتمد علىactivating or deactivating ديX على حسب Classification of groups Activating gps. Deactivating gps. Activating groups: they are groups which: -Cause the rate of electrophilic substitution to be faster than that of benzene. -Direct second substituent to ortho & para positions. This because they are: electron releasing substituent +I & +M. **Effect of +M is stronger than +I** Deactivating groups: they are groups which: -Cause the rate of electrophilic substitution to be slower than that of benzene. -Orientation is classified into: Clinical 2020 General Rule: Electron releasing substituent stabilizes carbocation & the reaction is faster (activation) & electron withdrawing substituent destabilizes carbocation & the reaction is slower (deactivation). Activation .بيزود عدد االلكترونات في البنزين Deactivation .بيقلل عدد االلكترونات في البنزين الليsubstituent هيActivated substituent . للبنزينe’s بتدي ”reactivity" بيخلي التفاعل أسرع . مستقر بحيث يكمل التفاعلcarbocationبيخلي الليsubstituent هيActivated substituent . من البنزينe’s بتسحب ”reactivity" بيخلي التفاعل بطئ . غير مستقرcarbocationبيخلي .+ve charge ألنه بيعوض .+ve charge ألنه مش بيعوض Clinical 2020 To summarize: Activating +I, +M "Ortho,para" Deactivating -I "Meta"& I, -M "Meta"& -I,-M "O,P" Activating o,p-directing group Alkyl grps. +I groups If I want to add more substituent to Alkyl benzene, where should it go? -Alkyl has +I effect which means it gives e’s and make benzene is activated. في2nd subs. وبتوجه ال، بتسرع التفاعل: بتعمل حاجتينactivated gp. احنا عرفنا إن .ortho,para position Clinical 2020 Why alkyl is weak activating group? Due to electron releasing +I effect of alkyl which increases electron density on the ring carbons so can be easily attacked by electrophile. The intermediates form o,p-attack have especially stable structure as +ve charge is adjacent to R group (tertiary carbocation) & so reaction is faster. The m-attack has no especially stable structure. ؟weak activating group بيكونAlkyl ليه .) على حلقة البنزين (شحنة سالبةelectrons يعني بيدوا الكترونات فبيزودوا كثافة ال+I effect علشان هم عندهم.) (شحنة موجبةelectrophile فيسهل الهجوم على+ve بمعنى إنespecially stable structure عندهo,p- position اللي إتكون فيintermediateونتيجة ده إن. ويبقى مستقر والتفاعل يبقى سريييع+ve charge وهي بتدي الكترونات فبتعوضAlkyl gp. بتكون جنبcharge مش+ve chagre بمعنى إنespecially stable structure ماعندوشmeta اللي إتكون عندintermediate أما. فيبقى صعب تعويضهاAlkyl بتكون جنب Clinical 2020 Activating o,p-directing group +M groups These groups have unshared electron pair on the atom attached to benzene so they have +M effect >>> its –I effect. E.g NH2 in aniline. Why aniline has high reactivity & o,p-directing? Because . The intermediate from o,p-attack have especially stable structure (stabilized by the strong electron donating resonance effect of NH2 (+M) so +ve charge is decreased so structure is more stable. This decrease in charge on intermediate doesn’t occur in the m-attack. وبتتصل بالبنزين زيlone pair وهم مجموعات عندها+M effect بس بسببActivating هنا هنتتكلم عن .aniline اللي في الNH2 ؟؟reactive and o,p-directing بيكونaniline ليه بكده يخلي.. يعني بيدي الكترونات فيزود كثافة االلكترونات في البنزين+M effect علشان عندهreactive هو.avtivated البنزين عندهمo,p-position اللي تكون فيintermediate علشان،،o,p-position أما ليه هو بيوجه عند+ve اللي بتدي الكترونات فهتعوض الNH2 هتكون جنب+ve charge يعنيespecially stable structure .stable structure ويبقىcharge .Meta دخل علىsubstituent إنها كده هتقل والنقصان ده مش موجود لو ال+ve charge معنى تعويض الYou should write first 2 equations in give reasons questions. Clinical 2020 Other activating group & has +M effect are: -R, -OR, -NHCOR, -OH, -OCOR, -NHR, NR2 . Deactivating m-directing groups Due to –I effect e.g. CF3, +NH3, NR3, CCl3. Why CF3 group is strong deactivating & m-directing? Due to CF3 group has –I effect so it deactivates all positions on benzene by increasing +ve charge on intermediate carbocation. It is m-directing due to: The intermediate formed by o,p-attack is unstable because there is +ve charge on the carbon bears electron withdrawing gp. The intermediate formed by m-attack has no stuch unstable structure so more stable than intermediate from o,p-attack. -I (meta position).. -I,-M (meta).. –I,-M : أسباب3 وليهاdeactivating gps. بنتكلم هنا على .(ortho,para) .(withdrawing( e’s يعنى بيسحبوا: Deactivating m-directing due to –I effect أول نوع ؟strong deactivating & m-directing يعتبرCF3 ليه لكل االماكن على البنزين نتيجة زيادةDeactivating فبيعملe’s يعني بيسحب-I effect عشان هو عنده-1 . والشحنة دي مش بتتعوض وبكدة البنزين مش هيبقى مستقرintermediate الشحنة الموجبة على مش مستققر نتيجة وجود شحنة موجبة جنب الكاربونp,o-position اللي تكون فيintermediate عشان-2 بيكون أكثر استقرارا من الليm-position اللي تكون فيintermediate لكنe’s اللي بتسحبCF3 المتصلة بـ .o,p-poisiton تكونوا في Clinical 2020 Deactivating m-directing groups Due to –I & -M effect These gps. Have multiple bonds e.g NO2 group. Why NO2 group is deactivating meta-directing ? Beacause it is deactivating due to –M & -I effect. NO2 is electron is withdrawing gp. So destabilizes intermediate carbocation by increasing +ve charge. It is m-directing due to: The intermediate formed from o,p-attack is unstable due presence of ounstable reasonance structure due to adjancency of the +ve charge to carbon bears electron withdrawing group but intermediate from m-attack is relatively more stable than from m-attack o,p-attack. –I & -M علشانdeactivating m-directing group ثاني نوع ؟؟deactivating m-direction بتكونNO2 ليه مش مستقر نتيجة زيادةintermediate بيخليe’s – يعني بتسحبI & -M علشان عندهاdeactivation هي بتكون. وعدم تعويضها+ve charge مش مستقر نتيجة وجود شحنة موجبةo,p-position اللي إتكون فيintermediate علشانM-directing هي بتكون.e’s – يعني بتسحبI & -M اللي عندهاNO2 جنب الكربون المتصلة بـ مش جنب الكربون+ve charge بيكون أكثر استقرارا علشانmeta-postition اللي إتكون فيIntermediate أما ال. electron withdrawing gpالمتصلة ب Clinical 2020 Halogens (weak deactivating o,p-directing) Why ?? Halogen has –I > +M effect. +M effect of halogen is weaker than OH & NH2 because p- orbital of carbon & halogen are of different size carbon 2p orbital of carbon but Cl has 3p orbital, Br has 4p orbital & I has 5p orbital. So overlapping between them (2p-3p or 2p-5p) is less effective than 2p-2p overlap (between C & N or O). deactivating ،،weak ،،ortho,para-directing ،، –I & +M عندهاHalogen ثالث نوع Clinical 2020 -1هالوجين بيكون o,p-directingعشان عندهم +M effectفلذلك intermediateاللي بيتكون في o,p-position اكثر استقرارا من اللي إتكون في .m-position -2الهالوجين بيكون weakعلشان +M effectبتاعتهم أقل من تأثير +Mبتاعة OH & NH2ليـــــــه؟؟ بيقولك يا كبير علشان p-orbitalاللي عند الكربون والهالوجين مختلفين في الحجم ،الكربون عنده 2p-orbitalأما الهالوجين Cl, Br, Iعندهم 3p, 4p, 5pبالترتيب...يعني في فرق في الطاقة بين الهالوجين والكربون. لذلك overlappingبينهم هيكون ” “2p-3p, 2p-4p, 2p-5pواللي لها تأثير أقل اللي بين الكربون والنيتروجين أو االكسجين .2p-2p -4هنا بيكونوا deactivatingعشان في الحالة دي تأثير –Iأعلى من +Mوده الختالف حجم ال.orbital Orientation in disubtututed benzene هنا هنتكلم على مكان third substituentوده بيتحدد بتأثير كل من ،first & second substituentsهنا بقلى هنشوف ثالث حاالت: الحالة األولى = لما نالقي إن 2 groupsبيوجه the thirdفي مكان مشترك..احنا عارفين إن CH3بتوجه & ortho paraأما NO2بتوجه في .Meta Clinical 2020 الحالة الثانية = لما 2 groupsكل واحد يوجه في اتجاه ،بحدد على حسب األقوى بمعنى إن األقوى هو اللي يحدد مكان .3rd substituent احنا عارفين إن كل من CH3 & NH2بيوجه في .ortho & paraهنالقي إنهم مختلفين..فهنشوف مين األقوى وهنالقي إن NH2يبقى ،strong activatingعشان CH3يعتبر weak.activating فبكدا هناخد NH2ألنه األقوى.**ده سؤال ممكن ييجي وممكن ييجي سؤال مهم بيقول substituentهيدخل فين وأنا أحدد السهم “Mention by ”arrows the position of substituents Steric effect: Clinical 2020 هنا هنشوف المكان اللي مافيهوش زحمة يعني فين األفضلية بمعنى إن 3rd substituentممكن يدخل فين من األماكن الفاضية..وهيفضل المكان األفضى عن الزحمة. بكدة نكون خلصنا محاضرتنا وجزء ال Arenesهيتشرح مع المحاضرة الجاية. Clinical 2020