Problem set 3
advertisement

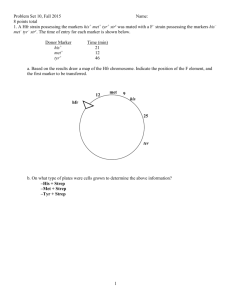
Problem set 3 8. Consider the following Hfr strains. In what order would the genes be transferred in an interrupted mating experiment in each case? 9. In E. coli, four Hfr strains donate the following markers, shown in the order donated: What is the order of these markers on the circular E. coli chromosome? 10. A cross is made between two E. coli strains: (Hfr arg+ bio+ leu+) x (F− arg− bio− leu−). Interrupted-mating studies show that arg+ enters the recipient last, so arg+ recombinants are selected on a medium containing biotin and leucine only. These recombinants are tested for the presence of bio+ and leu+. The following numbers of individuals are found for each genotype: Draw the gene order in the Hfr strain. Start with the Hfr itself. 11. Five Hfr strains A through E are derived from a single F + strain of E. coli. The following chart shows the entry times of the first five markers into an F− strain when each is used in an interrupted-conjugation experiment: a. Draw a map of the F+ strain, indicating the positions of all genes and their distances apart in minutes. b. Show the insertion point and orientation of the F plasmid in each Hfr strain. 12. Assume that you crossed two strains. The Hfr donor was Streptomycin sensitive (StrS) passed the lac+ genes early. The recipient was Streptomycin resistant (StrR) and lac-. The other genes to be tested on the donor were Nal+(naladixic acid resistance), Vir+ (virus resistance), Leu+ and His+. The recipient besides being StrR and Lac-, was Nal-, Vir- Leu- and His-. After mating the two strains for 100 minutes, you plated on M9 + lactose + Strep and collected 1000 Lac+ colonies. These were each tested for their phenotypea on a set of plates and you found the following: Total Lac+ colonies Lac+ His- NalLac+ His- Nal+ Lac+ His+ Nal+ Lac+ His+ Nal+ Lac+ His+ Nal+ VirVirVirVirVir+ LeuLeuLeuLeu+ Leu+ 1000 30 31 261 99 579 A. Write the order of genes on the donor chromosome, and their distances apart, assuming the lac region was transfered first, 5 minutes after the mating started. B. Why was streptomycin included in the plates that the orignal mating was plated on? C. What kind of plate would you use to test if colonies were Leu+ 13. Assume you had the following strains: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Lac+ Lac+ LacLacLac+ Lac+ LacLac- Met+ MetMet+ MetMet+ MetMet+ Met- StrR StrR StrR StrR StrS StrS StrS StrS Hfr Hfr Hfr Hfr Now assume that you did the following matings and plated the mix on M9 minimal plates with lactose + Strep. Indicate which would show a decent (> 50) number of colonies on the plate. Strain 1 x Strain 6 Strain 4 x Strain 8 14. map Hfr why Strain 2 x Strain 6 Strain 4 x Stain 7 Strain 2 x Strain 7 Strain 4 x Strain 5 A microbial geneticist isolates a new mutation in E. coli and wishes to its chromosomal location. She uses interrupted-mating experiments with strains and generalized transduction experiments with phage P1. Explain each technique, by itself, is insufficient for accurate mapping. 15. Imagine that you have a trpA mutant which is unable to grow unless tryptophan is provided in the medium. If the reversion rate is 10-8 revertants per cell and you plate 109 cells how many colonies will show up on a M9 minimal plate. If a trpA trpB double mutant has the same reversion rate for each mutation as the single mutant, how many cells would you have to plate, on average to see one colony on a minimal plate? If you could grow a culture up to 109 cells per ml, how many liters would you have to grow and plate in order to find this one Trp+ colony? Does this shed any light on why Lederberg used double mutants when trying to fix mutations by mating and recombination? 16. Imagine that you are studying a newly discovered species of fungi that forms fruiting bodies and spores. You have isolated a collection of mutants that don’t sporulated when plated by themselves, but that do sporulate when mixed with wild type. Having been and enthusiast of the elegant genetics done in M. xanthus, your are ready to try putting your mutants into complementation groups based on whether one mutant forms spores when mixed with another mutant. The data in the table below are the results of a mutant mixing experiment. The “+” means spores formed and the “-“ means that spores were not formed. How many complementation groups (genes or gene groups involved in a process needed or sporulation) are there? Which mutants are in each group? 17. Five new His- auxotrophs were isolated. Complementation analysis of each of the mutants gave the following results (+ indicates growth on minimal medium without histidine). 1 2 3 4 5 1 - 2 + - 3 + - 4 + + + - 5 + + + + - How many complementation groups are there? How many genes do the five His- mutants affect?