Lab: Enzyme activity and temperature and pH
advertisement

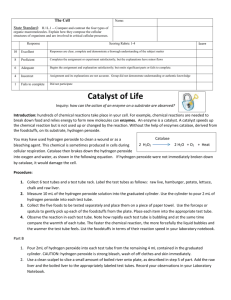
Physiology Lab: Enzyme Activity, Temperature and pH Background: Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up the rates of chemical reactions that take place within cells. In this investigation, you will study several factors that affect the activity of enzymes. The specific enzyme you will use is catalase, which is present in most cells and found in high concentrations in liver and blood cells. You will use liver as the source of catalase. Catalase promotes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in the following reaction: catalase 2 H2O2 ---------------------------- 2 H2O + O2 Hydrogen peroxide is formed as a by-product for chemical reactions in cells. It is toxic and soon would kill cells if not immediately broken down or removed. All cells produce an enzyme called catalase that will break down hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide is also used as an antiseptic. If you pour hydrogen peroxide on a cut, what do you observed? These observations are a result of catalase breaking down hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide is quickly broken down by the enzyme catalase as you will observe in this lab. Pre-Lab Questions: 1. What is the name of the enzyme being used in this lab? 2. What is the substrate in this lab? 3. What are the products in this lab? 4. What is in the liver that we are using in this lab? 5. How does the enzyme catalase help animals survive? PART 1 Write a hypothesis that addresses the following questions: Which temperature will cause the highest reaction rate of catalase with H2O2? Identify the Dependent Variable and Independent Variables Procedure: Room Temperature 1. Heat a beaker on a hot plate until boiling (this is your “bath”). 2. Put 1mL of liver in the bottom of each test tube. (Test tube 1, 2 and 3). 3. Add 3mL of hydrogen peroxide to each of the test tubes using a graduated cylinder. 4. Let the reaction proceed and then measure the height of the bubbles produced in mm in each of the test tubes. Record your result in your data table for Room Temperature. 5. Discard liquids in the sink and throw any liver in the trash can. Clean the test tubes. Procedure: Boiling 1. Put 1mL of liver in the bottom of each test tube. (Test tube 1, 2 and 3). 2. Put the test tubes in the boiling water bath for 10 minutes. (While you are waiting, begin part 2 on pH.) 3. After 10 minutes measure 3mL of hydrogen peroxide in your graduated cylinder . 4. Add 3mL of hydrogen peroxide to the liver in each of the 3 test tube that you boiled. 5. Measure the height of the bubbles in mm. Discard liquids in the sink and liver in the trash. Clean the test tubes completely. Data: Height of Bubbles (mm) Room Temperature Liver Test Tube 1 Test Tube 2 Test Tube 3 Average Boiled Liver Graph the trials and averages for both liver temperatures. Make only one graph comparing the two conditions. PART 2 Write a hypothesis that addresses the following questions: Which pH will cause the highest reaction rate of catalase with H2O2? Identify the Dependent Variable and Independent Variables Procedure: 1. Use pH paper to record the pH of H2O and HCl. 2. Put 1 mL of liver in the bottom of 3 test tubes. (Test tube 1, 2 and 3). 3. Add 10 drops of water to each tube. 4. Add 3 mL of hydrogen peroxide to each tube. 5. Measure the height of the bubbles in mm. . Discard in the sink. Clean the test tubes completely. 6. Repeat steps 2-5 using 10 drops of HCl instead of water. Data: Water pH = Height of Bubbles (mm) HCl pH = Test Tube 1 Test Tube 2 Test Tube 3 Average Graph the trials and averages for both pH solutions. Make only one bar graph comparing both conditions. Analysis Questions: 1.) Explain how an enzyme and a substrate work together? 2.) What information can you determine from your graphs? Explain your results for the two different procedures. 3.) Most enzymes are proteins. What do you think happened to catalase based on your data when you heated it up and then when you added HCl? 4.) What are the various factors that affect enzyme activity? Explain how each works. 5.) Why do you think this lab activity is important in understanding metabolic reactions in the human body? Conclusion: Write a summary of the knowledge you gained from this experiment. Re-visit your two hypotheses and state whether or not you proved them correct. Draw any new found conclusions.