Enzyme Lab
advertisement

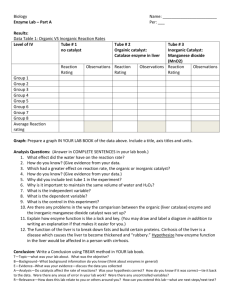
ENZYME LAB Introduction: What is a decomposition reaction? What are enzymes? Purpose: To become familiar with some of the characteristics of enzymes. Materials: hydrogen peroxide - 3% approx. copper metal raw fresh potatoe calf liver MnO2 powder beaker hot plates thermometer candle, matches test tubes mortar and pestle applicator sticks (splints) Procedure: 1. Clean 8 large test tubes. 2. Number the test tubes from #1 to #8 and place in a suitable rack. 3. Add approximately 4 mL of hydrogen peroxide to each test tube. 4. Carefully add the following to the test tube and record ALL results: #1. nothing (do you really need to do this one???) #2. a pinch of manganese dioxide #3 a small piece of copper #4. a piece of liver (10 mm X 10 mm x 10 mm) #5. crushed liver, the same size as in #4 #6. boiled liver (5 min.), same size as in #4 #7. fresh potatoe, same as in #4 #8. A small pinch of catalase (if available) 5. Record the temperature of the hydrogen peroxide before and after adding the pieces of liver (crushed and raw). There will be a temperature change. Temperature will increase after adding the liver. 6. Repeat #4, adding raw liver and test to determine if the gas evolved is something you know??? Do a splint test. Splint test will show that oxygen has been released. 7. Clean up your equipment, clean our foreign matter from the sinks!!!!! Discussion Questions 1. Rank the reactions for #1 to #8 using a scale that shows the varying rates of reactions that you observed. (1 to 5) (A B..F) (none….wild) A (no reaction) →C (wild reaction) Test tube #1. Test tube #2. Test tube #3 Test tube #4. Test tube #5. Test tube #6. Nothing – no reaction, this is the control – A a pinch of manganese dioxide – forms water and oxygen – B a small piece of copper – produced gas and dissolved – B a piece of liver (10 mm X 10 mm x 10 mm) – produced gas – C crushed liver, the same size as in #4 – produced gas – C boiled liver (5 min.), same size as in #4 – no reaction – A Test tube #7. fresh potatoe, same as in #4 – produced gas – C Test tube #8. A small pinch of catalase (if available) – produced gas – C 2. Is MnO2 an enzyme? Is it a catalyst? How could you prove if it is a catalyst? Manganese dioxide is a catalyst because it is not used up in reactions. 3. Write a balanced equation for the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. 2H2O2(aq) -------------------> 2H2O(l) + O2(g) + catalase(aq) 4. How could you prove if the enzyme in liver is reusable? The reusability of catalase can be tested by pouring hydrogen peroxide over a used piece of liver. The result would be positive, a reaction occurs. Hence, the liver is reusable. 5. Try to determine the name of the enzyme in liver cells that is capable of decomposing hydrogen peroxide. The name of the enzyme in liver cells is catalase. 6. What is denaturation? Did it happen in this lab? What are other ways to denature an enzyme? Denaturation is when an enzyme loses some to all of its function because of a change in environmental conditions. In this lab, catalase was denatured by a change in temperature. Enzymes can also be denatured by changes in pH levels. 7. Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? How do you know? The reaction was exothermic because an increase in temperature indicated that heat was released. 8. Prepare a simple procedure that could be followed to show the effect of temperature on the rate of enzyme activity? - Use pepsin to break down egg white. Add pepsin to egg white in a beaker. Egg white is cloudy, but when pepsin is added at the right pH and temperature it will turn clear, meaning that the pepsin enzyme has broken down the egg white into smaller protein molecules. Place a white piece of paper with a “x” drawn on it under the bottom beaker. Time how long it takes for the ‘x” to become clearly visible. BONUS: What are some applications of enzymes? - Proteases are used in production of white bread, buns, and rolls. - Trypsin is used to predigest baby foods. - Amyloglucosidase is used in low-calorie beer. - Cellulases and pectinases clarify fruit juices. - Amylases used in detergents for machine dish washing to remove resistant starch residues. - Lipases are used to assist in the removal of fatty and oily stains. - Catalase is used to generate oxygen from peroxide to convert latex into foam rubber.