Chapter 15 and 16 Study guide
advertisement

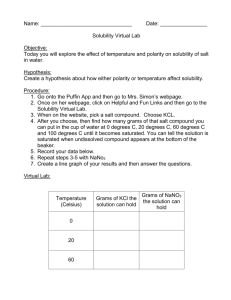
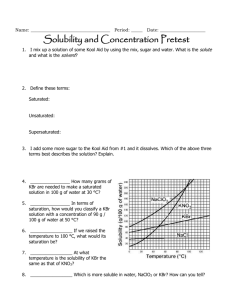
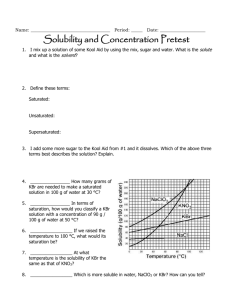
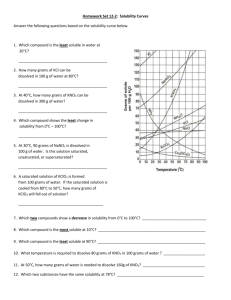
Name:______________________________________________________Date:___________Period:_______ Chapter 15 & 16 Study Guide BIG IDEAS: Here is a list of the big ideas you read about in this chapter: Water’s Unique properties in the liquid state versus Water unique properties in the solid state (pages 445-449) o Know water’s unique properties and WHY it has it’s unique properties o Know the structure of water and why it forms hydrogen bonds o Know the difference between the liquid water and solid water and WHY they are different Example Questions: 1. The diagram on the right depicts a collection of water molecules. Draw dotted lines showing where hydrogen bonding occurs. 2. Explain three ways hydrogen bonds affect the properties of water. 3. The diagrams on the right show hydrogen bonding between water molecules. a. Which diagram depicts ice? _______ b. Which diagram depicts liquid water? ______ 1 c. Why is ice less dense than liquid water? 2 Name:______________________________________________________Date:___________Period:_______ Properties of Solutions (Pages 471-477) o o o o o o o o o Define and explain the solvation process (page 451) Define solute, solvent, and solution. Know how they are related to each other Know the 3 factors that affect the dissolving of solutions Define solubility Define saturated, unsaturated, supersaturated Read and use the solubility graph Define miscible and immiscible: Know the significance of “like dissolves like” Explain how temperature affects the solubility of solids, liquids and gases Explain how pressure affects the solubility of solids, liquids, and gases 4. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. Immiscible Liquid Soluble Solution Insoluble Miscible Solute Solvent Air is a(n) ________________ of oxygen gas dissolved in nitrogen gas. The oxygen in air is the ________________, and the nitrogen is the ________________. Because oxygen gas dissolves in a solvent, oxygen gas is a(n) ________________ substance. A substance that does not dissolve is ________________. ________________ solutions are the most common type of solutions. If one liquid is soluble in another liquid, such as acetic acid in water, the two liquids are ________________. However, if one liquid is insoluble in another, the liquids are _______________. (page 451) 5. As sodium chloride dissolves in water, what happens to the sodium and chloride ions? What is this process? 6. How does the strength of the attraction between water molecules and sodium and chloride ions compare with the strength of the attraction between the sodium ions and chloride ions? How do you know? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 7. Name three factors that influence the rate at which a solute dissolves in a solvent. _____________________, ___________________________, ___________________________ Name:______________________________________________________Date:___________Period:_______ 8. Is the following sentence true or false? Justify your answer. Finely ground particles dissolve more rapidly than larger particles because finer particles expose a greater surface area to the colliding solvent molecules. Answer: ____ Justification: ________________________________________________________ 9. The amount of a substance that dissolves in a given quantity of solvent at a constant temperature is called the substance’s ______________________ at that temperature. 10. Look at Figure 16.3 on page 473. Why does the oil float on the vinegar? (meaning, why are oil and water immiscible?) ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 11. How does the solubility of solid substances change as the temperature of the solvent increases? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 12. How does the solubility of a gas change with an increase in temperature? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 13. Fill in the following chart using the general rule, “like dissolves like” Substance Ionic or Polar Covalent or Water or Oil Nonpolar Covalent a. CCl4 b. C3H8O c. LiCl d. CS2 Name:______________________________________________________Date:___________Period:_______ Use the graph below to answer the following 14. What is the solubility of KCl at 25C? __________________ 15. What is the solubility of Ce2(SO4)3 at 10C? _______ 16. Are the following solutions saturated, unsaturated or supersaturated (assume that all three could form supersaturated solutions) a. 40. g of KCl in 100 mL of water at 80oC _______________________ b. 120. g of KNO3 in 100 mL of water at 60oC _____________________ c. 80. g of NaNO3 in 100 mL of water at 10oC ________________ 17. Assume that a solubility curve for a gas such as ammonia, at one atmosphere of pressure, was plotted on the solubility curve graph. Reading from left to right, would this curve would ____________ a. slope upward b. slope downward c. go straight across 18. What is the smallest volume of water, in mL, required to completely dissolve 39 grams of KNO3 at 10oC? (Hint: use ratios) 19. 30 grams of KCl are dissolved in 100 g of water at 45oC. How many additional grams of KCl are needed to make the solution saturated at 80oC? 20. Using the data from question 25, how many grams of KCl would dissolve in 350 g of water? Name:______________________________________________________Date:___________Period:_______ Concentration of Solutions (Pages 480-486, 491 o Define concentration, dilute solution, and concentrated solution o Define and calculate Molarity o Calculate dilute solutions o Calculate percent by volume o Calculate percent by mass o Calculate Molality 21. Calculate the molarity of each of the following solutions. a. 0.40 mol of NaCl dissolved in 1.6 L of solution b. 20.2 g of potassium nitrate, KNO3, in enough water to make 250.0 mL of solution 22. Calculate the number of grams of solute needed to prepare 2500.0 mL of a 3.0M solution of potassium hydroxide, KOH. 23. What is the concentration in percent by volume, %(v/v), of the following solution? a. 60.0 mL of methanol in a total volume of 500.0 mL 24. How many grams of solute are needed to prepare 1.00 L of a 3.00% (m/m) NaCl solution? Colligative Properties (pages 487-490 & 494-496) o Define colligative properties o Calculate boiling points and freezing points of electrolytes and nonelectrolytes 25. Calculate the freezing point of a solution containing 0.600 kg of CHCl3 and 42.0 g of eucalyptol (C10H18O), a fragrant substance found in the leaves of eucalyptus trees. (Kf of CHCl3 = 4.68 oC/m, normal freezing point = -63.5oC) 26. Calculate the boiling point of a solution containing 53.4 g of CCl4 and 1.23 kg of ethanol (CH3CH2OH, Kb = 1.22 oC/m, normal boiling point = 78.4 oC). 27. The more particles that ionize in solution the _______________ the colligative properties are affected .