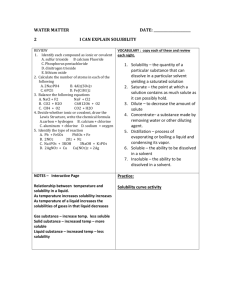
Content Map of Unit 10th Grade Conceptual Physics
advertisement
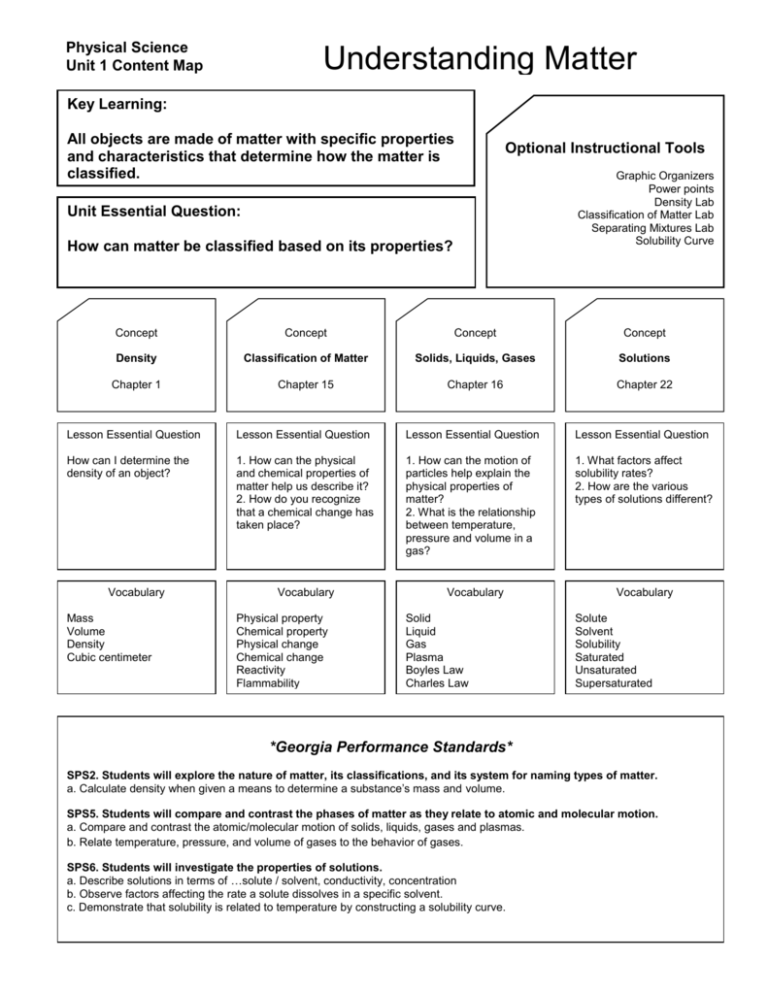
Physical Science Unit 1 Content Map Understanding Matter Key Learning: All objects are made of matter with specific properties and characteristics that determine how the matter is classified. Optional Instructional Tools Unit Essential Question: How can matter be classified based on its properties? Graphic Organizers Power points Density Lab Classification of Matter Lab Separating Mixtures Lab Solubility Curve Concept Concept Concept Concept Density Classification of Matter Solids, Liquids, Gases Solutions Chapter 1 Chapter 15 Chapter 16 Chapter 22 Lesson Essential Question Lesson Essential Question Lesson Essential Question Lesson Essential Question How can I determine the density of an object? 1. How can the physical and chemical properties of matter help us describe it? 2. How do you recognize that a chemical change has taken place? 1. How can the motion of particles help explain the physical properties of matter? 2. What is the relationship between temperature, pressure and volume in a gas? 1. What factors affect solubility rates? 2. How are the various types of solutions different? Vocabulary Mass Volume Density Cubic centimeter Vocabulary Physical property Chemical property Physical change Chemical change Reactivity Flammability Vocabulary Solid Liquid Gas Plasma Boyles Law Charles Law Vocabulary Solute Solvent Solubility Saturated Unsaturated Supersaturated *Georgia Performance Standards* SPS2. Students will explore the nature of matter, its classifications, and its system for naming types of matter. a. Calculate density when given a means to determine a substance’s mass and volume. SPS5. Students will compare and contrast the phases of matter as they relate to atomic and molecular motion. a. Compare and contrast the atomic/molecular motion of solids, liquids, gases and plasmas. b. Relate temperature, pressure, and volume of gases to the behavior of gases. SPS6. Students will investigate the properties of solutions. a. Describe solutions in terms of …solute / solvent, conductivity, concentration b. Observe factors affecting the rate a solute dissolves in a specific solvent. c. Demonstrate that solubility is related to temperature by constructing a solubility curve.