Unit 10 Review - Dakota Valley School
advertisement

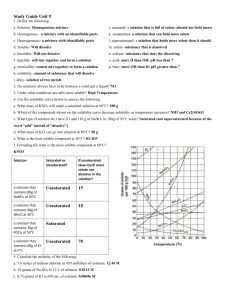
Unit 10 Review Name ____ Please answer the following questions in either red or blue. For any questions requiring work, complete on a piece of notebook paper to be turned in. 1. Describe the following terms in your own words: a. Solution: b. Solvent: c. Solute: d. Soluble: e. Insoluble: f. Miscible: g. Immiscible: 2. Give 4 examples of solutions (not just solids dissolved in liquids). Include 1 alloy (mixture of metals). a. b. c. d. 3. Describe what happens as a crystal of salt (NaCl) dissolves in water. 4. How is the dissolving process for sugar in water different from salt in water? 5. Why doesn’t oil dissolve in water? Would oil dissolve in anything? 6. What is solubility? 7. How does temperature affect solubility . . . a. For solids? b. For gases? i. What else changes gas solubility? 8. What three things can be done to increase the rate at which a solid dissolves? a. b. c. 9. Dissolving is a ( PHYSICAL / CHEMICAL ) change. (underline one) 10. How would you prepare a supersaturated sugar solution? Include the term “seed crystal”. 11. What is one test you could do to determine if a solution was unsaturated, saturated, or supersaturated? Describe how the results would be different for unsaturated, saturated, supersaturated solutions. 12. Water is known as the ____ ____. 13. What does solution concentration describe? 14. What do we use to describe solution concentration in chemistry? 15. If a solution is “strong” it is ____ and if it is “weak” it is ____. 16. What does it mean to dilute a solution? 17. What equation do we use for dilutions? ______________________ 18. When determining solubility remember, “ ____ dissolves ____.” 19. ( POLAR / NONPOLAR ) molecules will dissolve in water. (underline one) 20. Polar molecules: one of these shapes: ____, ____, and must have ____ bonds (electronegativity difference between 0.4-2.1) 21. Molecules that won’t dissolve in water include anything with ____ bonds (electronegativity differences less than 0.4) or symmetrical shapes such as ____, ____ or ____. These substances might dissolve in ____. SHOW WORK FOR #22 – 30 ON A SEPARATE PIECE OF PAPER! 22. What is the molarity of a sodium chloride solution that contains 1.73 moles in 3.94 L of solution? 23. What is the molarity of sodium hydroxide solution that contains 23.5 g NaOH In 500.0 mL of solution? 24. How many grams of potassium nitrate are in 275 mL of 1.25 M solution? 25. How many mL of 3.25 M hydrochloric acid would contain 16.0 grams of solute? 26. You have 12.0 M HCl in your stock room. How many milliliters of stock solution would you need to prepare 600.0 mL of 2.50 M HCl solution? 27. How would you correctly prepare 500.0 mL of a 3.0 M solution of NaOH from solid solute? 28. How would you prepare 500 mL of 3.0 M NaOH from 12.0 M concentrated stock solution? 29. An excess of zinc is added to 125 mL of 0.100 M HCl solution. What mass of zinc chloride is formed? Zn + 2 HCl ZnCl2 + H2 30. Determine whether or not the following chemicals will dissolve in water. JUSTIFY EACH ANSWER using Lewis structures and words! MgCl2 SeO2 SiO2 PCl3