Unpacking Outcomes - North East School Division
advertisement

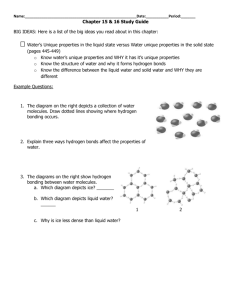
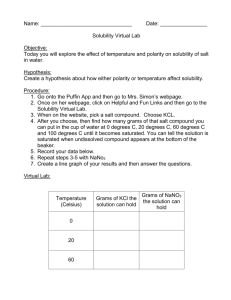
North East School Division Unpacking Outcomes Unpacking the Outcome Investigate properties and applications Outcome (circle the verb and underline the qualifiers) MS 7.3 Investigate the properties and applications of solutions, including solubility and concentration. KNOW UNDERSTAND BE ABLE TO DO Vocabulary – solid, liquid, gas, solvent, solute, soluble, insoluble, particle, theory, matter, solution, dilute, concentrated, saturated, supersaturated, quantitative, qualitative, accuracy, precision, honesty, interpolating, extrapolating, solubility curve Quantitative measures – parts per million [ppm], g/L, g/ 100mL How to: Design and implement an experiment Generate a solubility curve Gather information Analyze effects, inventions and processes Technological inventions or processes – water softeners, water treatment plants, solution mining, agricultural sprays, insecticides, bleaches, drain cleaners That accuracy, precision and honesty are essential when collecting and reporting data in order for good science to occur That solutions occur in solid, liquid and gaseous form Solutions have solvents and solutes and their concentrations can be measured quantitatively and qualitatively There are a number of factors that determine the speed of dissolving There are a number of place to gather information about solutions and concentrations, science disciplines and engineering fields Experiments help us answer questions Temperature impact solubility Patterns in data inform us in science Technological inventions and processes affect us, our communities and the environment There are science careers that apply solution-related information Provide examples of solid, liquid and gaseous solutions Identify which substance is the solute and which is the solvent in each solution Describe characteristics of solutions, using correct terms, using the particle model of matter Create and describe the concentration of studentprepared dilute, concentrated, saturated, and supersaturated solutions, using qualitative term and quantitative measures Value accuracy, precision and honesty when collecting and reporting data Investigate factors that determine how quickly a solute dissolves in a solvent Gather and interpret information from various resources related to solutions and concentrations of solutions Design and implement and experiment to investigate the effect of temperature on solubility Predict the solubility of a solute by interpolating or extrapolating from student-generated solubility curves Analyze the effects of technological inventions or processes related to solutions on self, community, environment Research how various science disciplines and engineering fields apply scientific knowledge related to solutions ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Why are accuracy, precision and honesty so important in science? How do solutions occur? What do we know about solutions? How is dissolving impacted by various factors? Where can I go for information? Why are a variety of sources important? Why experiment? How does temperature impact solubility? What can we learn from data? How do technological inventions and processes impact us, our communities and the environment? How do science careers use solubility and concentration in their work?