Topic XI – Solutions - Science - Miami
advertisement
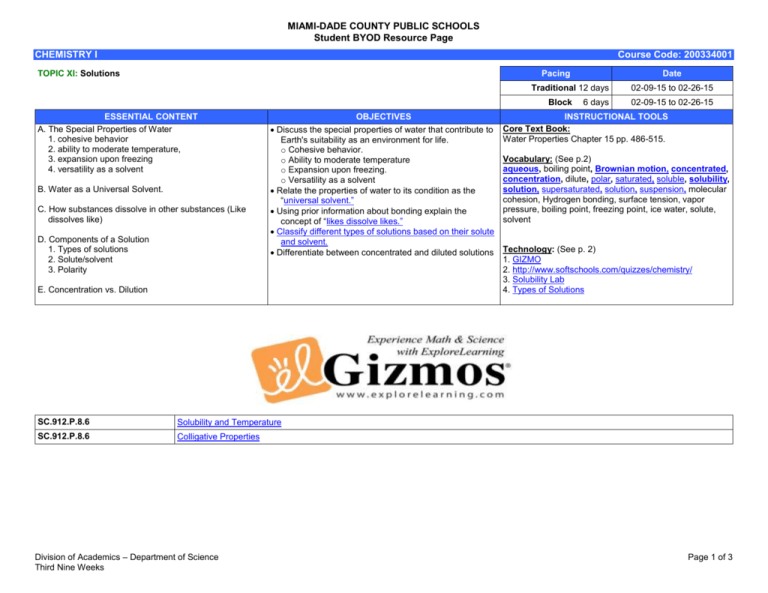
MIAMI-DADE COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Student BYOD Resource Page CHEMISTRY I Course Code: 200334001 TOPIC XI: Solutions Pacing Date Traditional 12 days Block ESSENTIAL CONTENT A. The Special Properties of Water 1. cohesive behavior 2. ability to moderate temperature, 3. expansion upon freezing 4. versatility as a solvent B. Water as a Universal Solvent. C. How substances dissolve in other substances (Like dissolves like) D. Components of a Solution 1. Types of solutions 2. Solute/solvent 3. Polarity OBJECTIVES Discuss the special properties of water that contribute to Earth's suitability as an environment for life. o Cohesive behavior. o Ability to moderate temperature o Expansion upon freezing. o Versatility as a solvent Relate the properties of water to its condition as the “universal solvent.” Using prior information about bonding explain the concept of “likes dissolve likes.” Classify different types of solutions based on their solute and solvent. Differentiate between concentrated and diluted solutions E. Concentration vs. Dilution SC.912.P.8.6 Solubility and Temperature SC.912.P.8.6 Colligative Properties Division of Academics – Department of Science Third Nine Weeks 6 days 02-09-15 to 02-26-15 02-09-15 to 02-26-15 INSTRUCTIONAL TOOLS Core Text Book: Water Properties Chapter 15 pp. 486-515. Vocabulary: (See p.2) aqueous, boiling point, Brownian motion, concentrated, concentration, dilute, polar, saturated, soluble, solubility, solution, supersaturated, solution, suspension, molecular cohesion, Hydrogen bonding, surface tension, vapor pressure, boiling point, freezing point, ice water, solute, solvent Technology: (See p. 2) 1. GIZMO 2. http://www.softschools.com/quizzes/chemistry/ 3. Solubility Lab 4. Types of Solutions Page 1 of 3 MIAMI-DADE COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Student BYOD Resource Page CHEMISTRY I Standard: SC.912.P.8.2 Standard: SC.912.P.8.6 Course Code: 200334001 Video Video Video Standard: SC.912.P.12.12 Math Explanation Standard: SC.912.L.18.12 Video Division of Academics – Department of Science Third Nine Weeks Particle Model of Matter: Solution Solutions and Solubility Dissolving Ionic Compounds Ionic Solutions Solution Formation Solubility Titration Calculations Percent Composition Intermolecular Forces Van Der Waal’s Repulsion States of Matter: Intermolecular Forces Dipole-dipole Bond Hydrogen Bonds in Water Hydrogen Bonding and Life Kinetics: The Speed of Chemical Reactions Dilutions What is a Diluted Solution? Expressing Concentration Concentration Molarity Molarity Titration Calculations Percent Composition Dilution: Example 1 Dilution: Example 2 Dilution: Example 1 Dilution: Example 2 Why is Water Essential to Life on Earth? Water's Molecular Structure Chemical Properties of Water Water and Plants: A Unique Water's Importance to the Origins of Life What's So Special about Water Relationship Page 2 of 3 MIAMI-DADE COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Student BYOD Resource Page CHEMISTRY I Course Code: 200334001 Video Image Why do we put salt on icy sidewalks in the winter? Sustainability: Water - The Water Cycle Sustainability: Water - Sierra Nevada Snow Pack & Snow Melt Glue With Mussels: Purdue Chemist Synthesizes Wet-Set Adhesive Use of Chemical Dispersants Made Oil More Toxic, Say Scientists The Dirt on Ammonia as a Cleaning Agent Molecule Profile: H2O - Water Avoiding the Dangers of Household Cleaners "Green" NC State Chemist Looks for Cleaner, Safer Fuel Process Division of Academics – Department of Science Third Nine Weeks Page 3 of 3