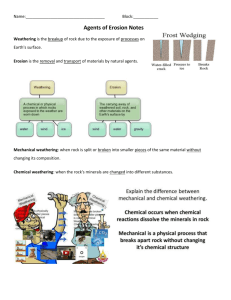
Cat Event, Ecoregions, WED and Watersheds Review Sheet
advertisement
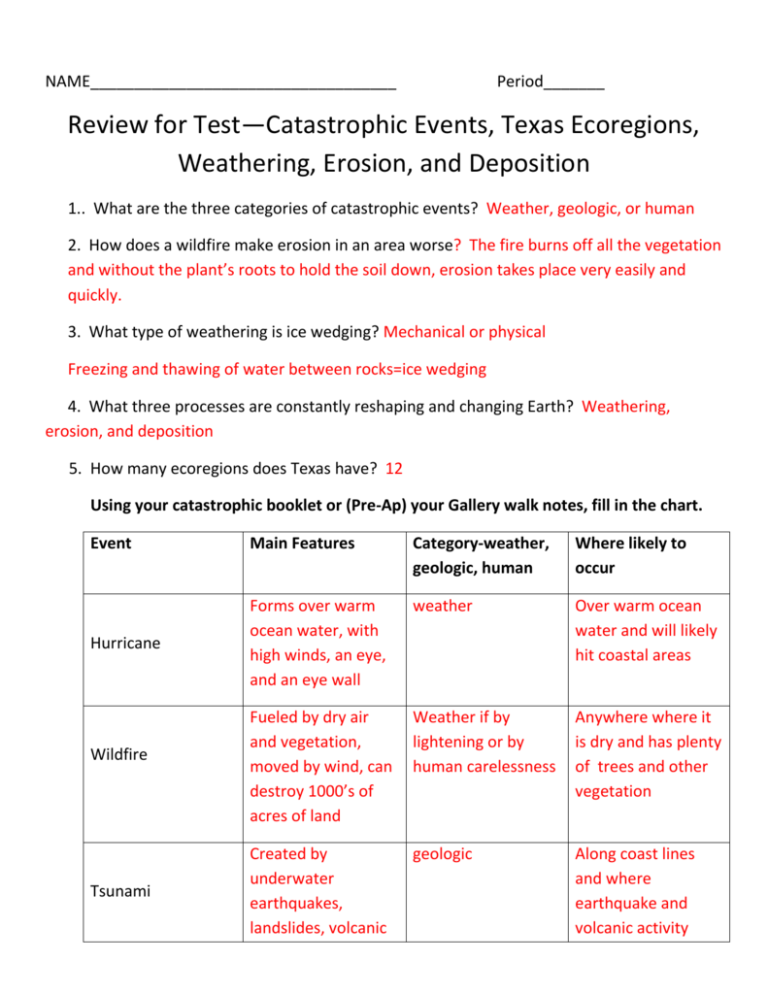
NAME___________________________________ Period_______ Review for Test—Catastrophic Events, Texas Ecoregions, Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition 1.. What are the three categories of catastrophic events? Weather, geologic, or human 2. How does a wildfire make erosion in an area worse? The fire burns off all the vegetation and without the plant’s roots to hold the soil down, erosion takes place very easily and quickly. 3. What type of weathering is ice wedging? Mechanical or physical Freezing and thawing of water between rocks=ice wedging 4. What three processes are constantly reshaping and changing Earth? Weathering, erosion, and deposition 5. How many ecoregions does Texas have? 12 Using your catastrophic booklet or (Pre-Ap) your Gallery walk notes, fill in the chart. Event Main Features Category-weather, geologic, human Where likely to occur weather Hurricane Forms over warm ocean water, with high winds, an eye, and an eye wall Over warm ocean water and will likely hit coastal areas Fueled by dry air and vegetation, moved by wind, can destroy 1000’s of acres of land Weather if by lightening or by human carelessness Anywhere where it is dry and has plenty of trees and other vegetation Created by underwater earthquakes, landslides, volcanic geologic Along coast lines and where earthquake and volcanic activity Wildfire Tsunami eruptions—huge wave height and speed occur. Using the class set of Texas cities, ecoregions, and data table, answer the following questions. 6. Name the 3 Texas cities most likely to be impacted by frequent wildfires. El Paso, Midland, and Odessa 7. Name 2 cities in north Texas most likely to be impacted by earthquakes. Amarillo and Lubbock 8. Which type of catastrophic event is the most common across the state of Texas? Wildfires 9. In what area (north, south, east, or west) would you expect to experience the highest number of tornados? north 10. Which type of catastrophic event do Texans NOT have to worry about? volcanoes Look at each statement and determine if it is an example of weathering, erosion, or deposition. Write either weathering, erosion, or deposition in the blank. 11. water freezing and thawing in rock cracks and breaking them apart-- weathering 12. rain washing away soil from a hillside--erosion 13. deltas forming at the mouths of rivers--deposition 14. ponds filling up with sediment and becoming marshes--deposition 15. flood water wearing down a canyon wall--weathering 16. wind blowing sand from one location to another--erosion 17. waves dropping sand on the beach--deposition 18. caves formed by acid rain dissolving underground limestone--weathering 19. flood water moving soil from one location to another--erosion Read this and answer the following questions. In a river there are several different sizes of sediment and rock. The sizes range from sand size, to gravel size, to small rock, to medium size rock, and to large size rock. 20. Which size sediment or rock will be picked up and moved first when the river first begins to flow? The smallest, in this case, the sand 21. Which size sediment will be deposited first when the river meets the ocean and slows down? The largest, in this case, the large size rock. 22. What is the name of the Ecoregion San Antonio is in? South Texas Brush/Plains 23. What is San Antonio’s source of water? Edward’s Aquifer 24. What is the largest watershed in the United States? Mississippi River Basin 25. What is the difference between mechanical and chemical weathering? Mechanical weathering is the physical force that breaks a rock. Chemical weathering is the wearing away of rock by oxidation or dissolving by acid 26. Explain what a watershed is. An area of land that drains runoff into a particular stream, lake, ocean or other body of water. 27. How are the boundaries of watersheds determined? By elevation. 28. Watersheds are connected by all the highest points in the area and determine the direction in which water flows when it hits the ground. 29. What does the term riparian habitat imply? A habitat that is near a river, lake, stream or body of water. 30. What is the difference between porosity and permeable? Permeability is a measure of the ability of water to flow through rock and sediment. Porosity is when an object is full of pores, tiny spaces and can hold water. 31. How do humans impact groundwater and surface water negatively? Give 3 examples and explain each of them. Answers will vary 32. How humans impact groundwater and surface water positively? Give 3 examples and explain each of them. Answer will vary 33. Give 3 examples of surface water. Lake, rivers, oceans, streams, ponds