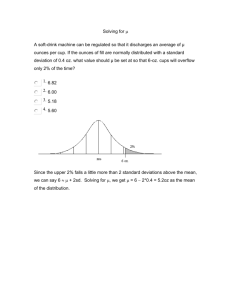
What are the assumptions for creating a population mean (μ
advertisement

Hypothesis Testing, Example 1: Bicyclists race on set route. The time of a cyclist drawn at random is randomly distributed with an approximately normal distribution with mean of 87 minutes and a standard deviation of 6 minutes. A bicycling coach claims to have a new training technique which will reduce times. We will test this claim by sampling 10 bicyclists who use this technique and measure their time on the same route. State the null hypothesis: State the alternative hypothesis: Is this a one tail or two tail test? If one tail, which? Since the standard deviation is given, we will use which statistic? We will use an alpha of 5%. What does this mean? What is the value of the critical value? Draw a bell curve to show the above. The sample of the 10 cyclists has a sample mean of 85 minutes. What is the resulting test statistic? What is the conclusion of the hypothesis test? What is the p-value? What does that mean? Hypothesis Test 2 Quality Control. Pyrex makes measuring cups. A “one cup” measuring cup must be able to measure a cup of liquid to within 2% of an actual cup. That is, a manufactured measuring cup should measure 8 ounces plus or minus 2% (=+/- .16 ounces). Assume any errors from one cup are distributed normally. A manufactured cup’s measurement has a mean of 8 ounces and a standard deviation of .12 ounces. QC person will test 5 measuring cups and test their accuracy. State the null hypothesis: State the alternative hypothesis: Is this a one tail or two tail test? If one tail, which? Since the standard deviation is given, we will use which statistic? We will use an alpha of 10%. What does this mean? What is the value of the critical value? Draw a bell curve to show the above. The sample of the 5 cups has a sample mean of 8.08 ounces. What is the resulting test statistic? What is the conclusion of the hypothesis test? What is the p-value? What does that mean?