1. Why is water a major agent of chemical weathering? A. Because
advertisement

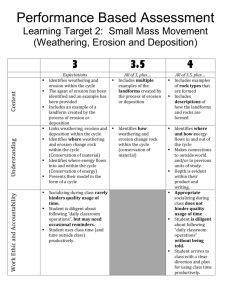
1. Why is water a major agent of chemical weathering? A. Because water cools the surroundings when it evaporates. B. Because water dissolves many of the minerals that make up rocks. C. Because water has a density of about 1 gm/cm3. D. Because water has the highest specific heat of all common Earth materials 2. Of the various types of mass movements, which is the slowest acting? A. rock slides B. debris flows C. slump D. creep 3. In which climate would the chemical weathering of limestone occur most rapidly? A. Cold and dry B. Cold and humid C. Warm and dry D. Warm and humid 4. What is the primary force responsible for most of the transportation of rock material on the surface of Earth? A. gravity B. wind C. running water D. glacial ice 5. How do glaciers erode the land? A. Through plucking and abrasion. B. Through wind and waves. C. Through gravity and waves. D. Through permeability and porosity. 6. How does the mass movement called slump occur? A. An entire piece of rock and soil breaks loose and surges downhill. B. A river carries away sediments. C. The wind blows very hard. D. Glaciers push the land forward. 7. What are two landforms created through wind deposition? A. Glacial lakes and oxbow lakes B. Sand dunes and loess deposits C. Meanders and cutoffs D. U-shaped valleys and V-shaped valleys 8. Why are slides the most devastating form of mass movements. A. Because they happen on hills. B. Because of the tremendous energy they get from their high speeds. C. Because people live near them. D. Slides are not the most devastating form of mass movements, creep is. 9. As the speed of a river increases, what happens to the size of the sediment particles that it can carry? A. As speed increases, particle size increases. B. As speed increases, particle size decreases. C. As speed increases, there is no change in the size of particles that are transported. D. It is not possible to tell what happens to particle size when the river speed increases. 10. Which of the following materials would be most likely to be carried by a slow moving stream? A. Pebbles B. Cobbles C. Sand D. Clay 11. A delta is an example of A. an erosion feature B. a depositional feature C. sandblasting D. abrasion 12. The removal and transportation of weathered rock sediments is known as A. weathering B. erosion C. deposition D. plate tectonics 13. A beach, sandbar, and spit are examples of A. erosion by waves B. deposition by waves C. erosion by wind D. deposition by glaciers 14. The breakdown of rocks at or near the surface of the Earth is known as A. weathering B. erosion C. deposition D. plate tectonics 15. What change will a pebble usually undergo when it is transported a great distance by streams? (a) It will become jagged and its mass will decrease. (b) It will become jagged and its volume will increase. (c) It will become rounded and its mass will increase. (d) It will become rounded and its volume will decrease. 16 Which type of rock was chemically weathered by acidic groundwater to produce the cave and its features? (a) siltstone (c) quartzite (b) basalt (d) limestone 17. The principal cause of the chemical weathering of rocks on the Earth’s surface is (a) rock abrasion (b) the heating and cooling of surface rock (c) mineral reactions with air and water (d) the expansion of water as it freezes 18. As water velocity (speed)decreases, the amount of sediment deposited (a) increases (b) decreases (c) remains the same 19. The satellite photograph to the right shows a geologic feature composed of silt, sand, and clay. The geologic feature shown in the photograph was primarily deposited by which agent of erosion? (a) glaciers (b) wind (c) wave action (d) running water 20. Soil is a mixture of all of the following EXCEPT……. a. weathered rock b. organic material c. erosion d. air 21. ______ is a mixture ranging from small particles to large boulders. A. sediment B. till C. deposition D. outwash 22. Mechanical weathering can result from the action of all of the following EXCEPT…… a. burrowing animals b. ice wedging c. carbonic acid d. plant roots 23. _______ is the result of sand and gravel deposits left by rivers. A. sediment B. deposition C. outwash D. till 24. Gravity, Ice, wind, and water are all agents of ____________. A. runoff B. erosion C. weathering D. abrasion 25. When materials containing iron are exposed to water and oxygen, _________ can occur. A. wedging B. ironization C. weathering D. oxidation 26. All of the following EXCEPT _________ can weather rock. A. animals B. sunlight C. plants D. freezing and thawing 27. Landforms such as plateaus, canyons, valleys, and cliffs are formed because of what process? A. weathering B. erosion C. deposition D. both a and b 28. Landforms such as deltas and beaches are formed because of what process? A. weathering B. erosion C. deposition D. both a and b 29. Which of the following area would experience the most erosion? A. an area with high winds, significant rain, hot summers, and freezing winters B. an area with heavy rains, constant temperatures, and gentle wind. C. an area with constant heat, minimal rain, and high winds. D. all areas are subject to the same amount of erosion. 30. Which human activity can help prevent soil erosion? a. planting crops b. strip mining c. deforestation d. building highways 31. The factors that affect the rate of weathering are…… a. microorganisms, plants, rainfall b. weather, landforms, and rainfall c. surface area, rock type, climate d. texture, color, shape 32. Which of the following is an example of erosion? a. glaciers slowly moving pieces of rock downward by gravity. b. a river carrying sediment to a delta c. sandstorms in the desert blowing grains of sand d. all of the above 33. When water or wind loses energy and drops the moving sediment, what process is occurring? A. weathering B. erosion C. deposition D. none of the above 34. As a river enters a lake or ocean, in which order will sediments be deposited? A. clay, silt, sand, pebbles B. sand, pebbles, silt, cobbles C. pebbles, boulders, sand, clay D. pebbles, sand, silt, clay