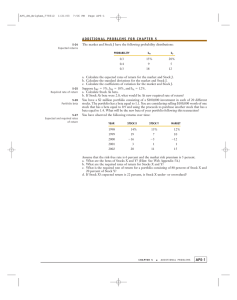
Chapter 10
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Estimating Risk and Return
Copyright © 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.1
Expected Returns
• Expected return is a forward-looking
calculation
• Includes risk measures
10-2
Expected Return
• Multiply each possible return by the
probability of that return occurring
10-3
Risk Premiums
• Required return is the return that investors
demand for the level of risk taken
• Risk premium is the reward investors require
for taking risk
• Market risk premium is the reward for taking
unsystematic stock market risk
10-4
The Market Portfolio
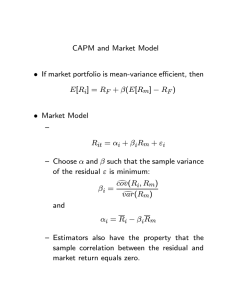
• Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)
– Best known capital asset pricing model
– Starts with modern portfolio theory
10-5
Efficient Frontier
• The efficient frontier demonstrates the
highest expected return for each level of risk
10-6
Efficient Frontier
• Adding a risk-free asset improves return for
each level of risk
10-7
CAPM
• Calculate the Security Market Line for
risk/return relationship
• Substituting into line equation results in
CAPM
10-8
Beta
• Measures the sensitivity of a stock or
portfolio to market risk
– Beta greater than 1 = more risky than market
(higher risk premium)
– Beta less than 1 = less risky (lower risk
premium)
10-9
Security Market Line
• Shows relationship between risk and return
for any stock or portfolio
• Similar to capital market line
– Risk is characterized by beta, not standard
deviation
10-10
Security Market Line
Uses Beta as Risk Measure
10-11
Portfolio Beta
Weighted average of portfolio stocks’ betas
10-12
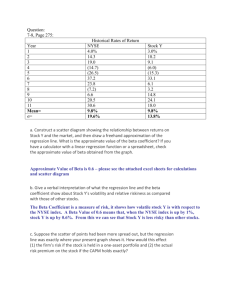
Finding Beta
• Two ways
– Can compute with data from company’s and
market portfolio returns
– Find in published data from financial outlets
10-13
Capital Market Efficiency
• Efficient markets feature
– Many buyers and sellers
– No high barriers to entry
– Free and available information
– Low trading or transaction costs
10-14
Efficient Market Hypothesis
• States that security prices fully reflect all
available information
• Three levels
– Weak form
– Semi-strong form
– Strong form
10-15
Weak-form Efficiency
• Current prices reflect all information derived
from trading
– Includes current and past stock prices and
trading volume
10-16
Semi-strong form Efficiency
• Current prices reflect all available public
information
– Includes information like financial statements,
news, analysts’ opinions
10-17
Strong-form Efficiency
• Current prices reflect all information
– Public
– Privately-held information
10-18
Behavioral Finance
• People behave in “irrational” ways
– Both optimism and pessimism can be
extreme
– Overconfidence is tendency to overestimate
knowledge and underestimate risk
10-19
Implications for Financial
Managers
• Managers must...
– understand the risk/return relationship and
implications
– address stockholders’ concerns and
requirements
10-20
Constant-Growth Model
• Assumes stock is efficiently priced
• Uses dividend and price data and forward
estimate
10-21