pure substance
advertisement

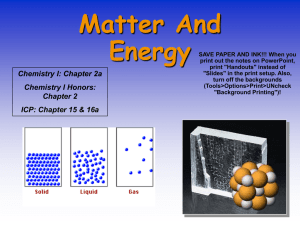
ANYTHING WITH MASS AND VOLUME Elements Pure Substances Compounds Matter Homogeneous Mixtures Heterogeneous Mixtures and Pure Substances • Matter that consists of two or more substances mixed together but not chemically combined is called a mixture. • A pure substance is made of only one kind of material and has definite properties. Elements • Elements are the simplest pure substance. – Examples: hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen. • The smallest particle of an element that has the properties of that element is called an atom. Compounds • A molecule is formed when two or more atoms combine. • Compounds are pure substances that are made of more than one element bound together. – Examples: water, table salt, and carbon dioxide. MIXTURES Heterogeneous vs. Homogeneous • Homogeneous matter: matter that has identical properties throughout. – Examples: Sugar, salt, water, and whipped cream • Heterogeneous matter: matter that has parts with different properties. – Examples: granite, soil, potpourri Conservation • Law of Conservation of Matter (Mass): matter cannot be created or destroyed. • Law of Conservation of Energy: Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it may only change from one form to another. Matter and energy MUST be conserved; it’s the LAW! Virtually everything that is, is made up of atoms. From the very large... To the very small... We are all made of atoms…and only atoms. This includes you and me! Currently we have about 115 kinds of atoms. In the natural world there exists 88 different kinds of atoms. The others have been artificially produced in laboratories. The Elements Song Making stuff nature never dreamed of. We call each kind of atom an element, and give it a specific name and symbol. Copper Gold Cu Au Periodic Table Abundance of the elements, by weight The Earth’s interior is rich in iron Sand is made of Silicon & Oxygen The ocean waters are made of oxygen & hydrogen Atoms are made up of protons, Of course real atoms neutrons, and electrons. don’t look anything like this! Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of atoms -- roughly at the center Electrons travel around the nucleus. Different kinds of atoms, or elements, are different because they have different numbers of protons. They don’t look anything like this either! We list the elements by their atomic numbers the number of protons they have. Hydrogen, number 1 Helium, number 2 Physical Properties • Physical properties: characteristics that can be observed without changing the identity of the substance. • Examples: – – – – – – mass volume color shape texture density Physical Changes • Physical change: a change in the physical form or properties of a substance that occurs without a change in composition. • Examples: – – – – melting freezing grinding dissolving Chemical Properties • Chemical property: describes a substance’s ability to change into a different substance. • Examples: – flammability – reactivity Chemical Changes • Chemical change: occurs when a substance changes composition by forming one or more new substances. (bonds are broken and bonds are formed) • Example: – HCl + NaOH NaCl + H2O Indications of a Chemical Change… Flames Gas is given off (not to be confused with boiling) Color Change Evaporation is a physical change Breaking is a physical change. Boiling is a change of state, and therefore a physical change! Rusting is a Chemical Change Burning is a Chemical Change Kinetic Theory • All matter is made of atoms and molecules that act like tiny particles. • These tiny particles are always in motion. The higher the temp., the faster the particles move. • At the same temp., more massive (heavier) particles move slower than less massive (lighter) particles. SOLIDS • Definite shape? • YES • Definite volume? • YES • Molecules in a solid are tightly packed and constantly vibrating. LIQUIDS • Definite shape? • NO • Definite volume? • YES • Some liquids flow more easily than others. The resistance of a liquid to flow is called viscosity. – Honey has a high viscosity compared to water. GASES • Definite shape? • NO • Definite volume? • NO • The particles in a gas are spread very far apart, but can be compressed by pumping them into a restricted volume. Phase Changes • Changes in phase are examples of physical changes. • • • • • Melting: solid liquid Freezing: liquid solid Vaporization: liquid gas Condensation: gas liquid Sublimation: solid gas Changes of State GAS Vaporization Sublimation Condensation Deposition Melting LIQUID Melting Freezing SOLID • ENERGY is the ability to change or move matter. • Energy is ABSORBED when substances melt or evaporate. – NOTE: our bodies cool down when our sweat evaporates. • Energy is RELEASED when substances freeze or condense. Melting • The change of state from solid to liquid. • Energy (heat) is absorbed by the substance that is melting. Freezing • The change of state from liquid to solid. Opposite of melting. Energy (heat) is released by the substance undergoing freezing. • Evaporation The change of state at the surface of a liquid as it passes to a vapor. This results from the random motion of molecules that occasionally escape from the liquid surface. – Energy (heat) is released by the liquid (Cooling of the liquid results) – Can happen at any temperature Condensation • The change of state from gas to liquid. The opposite of evaporation. – Energy (heat) is absorbed by the liquid (Warming of the liquid results) Boiling • Change from state from a liquid to a gas. • Occurs throughout the liquid. – boiling point/temperature is determined by pressure – Energy (heat) is released by the liquid. *Boiling & freezing points depend on the pressure. Water at normal pressure (1 atm): • For water at normal (every day) pressures: • Melting/freezing point: 0 oC (32oF) • Condensing/boiling point: 100 oC (212oF) Label the points & temperatures on your graph. Change the pressure Change the Boiling Point Phase Diagrams • a phase diagram shows the equilibria pressuretemperature relationship among the different phases of a given substance WATER Carbon Dioxide C AB = AC = AD = C melting AB = curve AC = AD = C melting AB = curve sublimation AD = AC = curve C melting AB = curve vapor sublimation AD = pressure AC = curve curve C A triple point = Point ______ The point at which all 3 phases of a substance (solid, liquid, gas) can coexist at equilibrium. D critical point = Point ______ The combination of critical temperature and critical pressure. critical temp = temp. above which a gas cannot be liquefied. (H2O=374ºC) critical pressure = press. required to liquefy a gas at its critical temperature. (H2O=218 atm) Conditions for H2O on other planets…