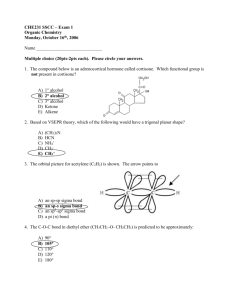
ORAL HYPOGLYCEMIC AGENTS
advertisement

ORAL HYPOGLYCEMIC AGENTS
Moustafa K. Soltan
Oral hypoglycemics
are used in NIDDM, in which insulin is still produced in the body but in lesser
amounts than required for normal glucose level adjustment, oral hypoglycemic has
no effect on the blood glucose level in case of absence of insulin, but they may be
used in case of IDDM to potentiate the action of exogenously administered insulin.
Insulin is a hormone that is synthesized, stored and excreted in β-cells of islets of
langerhanz in pancreas
.
They are two classes: 1) sulphonylyreas. 2) biguanides.
Sulphonyl urea derivatives.
R1
C4H9
C4H9
C3H7
R2
CH3
NH2
Cl
CH3
N
O
Generic name.
Tolbutamide.
Carbutamide.
Chloropropamide.
Tolazamide.
Acetohexamide.
H3C
Gliclazide
(diamicron)R
1-[3-azabicyclo[3.3.0]oct-3-yl]
-3-(p-tolylsulphonyl)urea.
****[3-azabicyclo[3.3.0]oct-3-yl] =
[cyclopentano[C]pyrrolidin-1-yl]
Glyboride
( glibenclamide)
(doanil)R
*5-chloro-N-{2-[[[[(cyclohexylamino)
carbonyl]amino]sulphonyl]phenyl]ethyl}-2methoxybenzamide.
*1-cyclohexyl-3-[p(5-chloro-2-methoxybenzamidoethyl)
phenylsulphonyl]urea.
R2= CH3
Cl
O
N CH2CH2
H
OCH3
Chemical nomenclature.
1-butyl-3-(p-tolylsulphonyl)urea.
1-butyl-3-(p-aminophenylsulphonyl)urea.
1-propyl-3-(p-chlorophenylsulphonyl)urea.
1-(hexahydro-1h-azepin-1-yl)-3-(ptolylsulphonyl)urea.
1-[3-(p-tolylsulfonylphenyl) uriedo]
hexahydro-1H-azepine.
1-cyclohexyl-3-[(pacetylphenyl)sulphonyl]urea.
Mode of action of sulphonylurea: 1) increase release of insulin from the β-cells of
pancreas.
2) decrease glycogenolysis. (glycogen to
glucose).
3) potentiate insulin.
*Structure activity relationships (SAR):
1) R1 must be of certain size so as to increase the lipophilicity of the molecule, so
control absorption, activity.
R1 = CH3 give inactive , R1 = C2H5 some activity, maximum activity from 3-6
carbon atoms,
R1= aryl groups yields toxic compounds.
2) R2 influence the duration of action of the compound, and the easiness by which
the compound can be metabolized so:
** Carbutamide (NH2) < tolbutamide (CH3) < chloropropamide (Cl) in duration
of action as amino group is easily metabolized than methyl group than chloro.
** acetyl as R2 and cyclohexyl as R1 as in acetohexamide increase the activity
to twice that of tolbutamide, really the rate of metabolism of acetyl group is slow
what cause duration of action of acetohexamide longer.
** R2 should be in para position.
Biguanides.
Phenformin
1-( -phenylethyl) biguanide HCl
Metformin
1,1-dimethylbiguanide HCl
Mechanism of action:
1) have no effect on β-cells, but increase glucose uptake by cells,
2) increase intracellular glycogen.
3) decrease carbohydrate absorption from the GIT so used in REGIME
Structure activity relationship:
1) R1may be alkyl group, activity is maximum when R1 is amyl (PENTYL)
group.
2) R1 may be aralkyl group, good activity obtained when it is benzyl or βphenethyl.
3) R2 should be H but methyl group may sometimes show activity.
* Synthesis of phenformin:
NH
NH
+
NH2
2-phenylethylamine
N C NH NH2
cyanoguanidine
phenformin
N
H
N
H
NH
NH2