Thermochemistry Worksheet: Enthalpy & Heat Calculations
advertisement

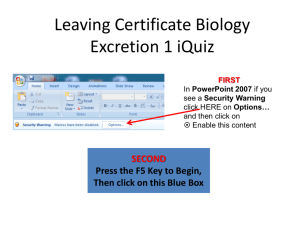
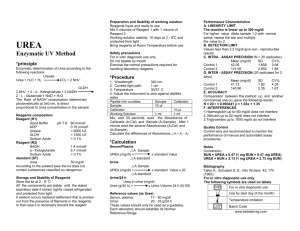
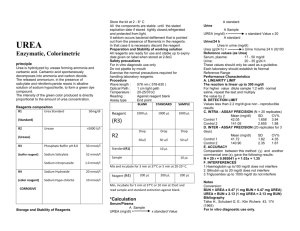
Name_______________________________ 1. The bombardier beetle uses an explosive discharge as a defensive measure. The chemical reaction involved is the oxidation of hydroquinone by hydrogen peroxide to produce quinone and water: C6H4(OH)2(aq) + H2O2(aq) C6H4O2(aq) + 2H2O(l) Calculate H for this reaction from the following data: C6H4(OH)2(aq) C6H4O2(aq) + H2 (g) H = +177.4 kJ H2(g) + O2(g) H2O2(aq) H = -191.2 kJ H2(g) + ½ O2(g) H2O (g) H = -241.8 kJ H2O(g) H2O(l) H = -43.8 kJ 2. A hot air balloon is being inflated to its full extent by heating the air inside it. In the final stages of this process, the volume of the balloon changes from 3.5 x 106 L to 4.50 x 106 L by the addition of 13 MJ of energy as heat. Assuming that the balloon expands against a constant pressure of 1.2 atm, calculate E for the process. To convert between L atm and J, use 1 L atm = 101.3 J. 3. For the reaction S(s) + O2(g) SO2(g) H = -296 kJ/mol a. How much heat is evolved when 2.5 mol sulfur is burned in excess O2? 4. Answer the following questions on thermochemistry: Substance Combustion Reaction H2(g) H2(g) + ½ O2(g) H2O(l) Enthalpy of Combustion, Hocomb, at 298 K (kJ mol-1) -290 C(s) C(s) + O2(g) CO2(g) -390 CH3OH(l) -730 a. In the empty box in the table above, write a balanced equation for the complete combustion of one mole of CH3OH(l). Assume products are in their standard states at 298 K. Coefficients do not need to be whole numbers. b. On the basis of your answer to part “a” and the other information in the table, determine the enthalpy change for the reaction C(s) + 2 H2(g) + ½ O2 (g) CH3OH(l) . 5. A student performs an experiment to determine the molar enthalpy of solution of urea, H2NCONH2. The student place 91.95 g of water at 25oC into a coffee-cup calorimeter and immerses a thermometer in the water. After 50 s, the student adds 5.13 g of solid urea, also at 25oC, to the water and measures the temperature of the solution as the urea dissolves. A plot of the temperature data is shown in the graph below. a. Determine the change in temperature of the solution that results from the dissolution of the urea. b. According to the data, is the dissolution of urea in the water an endothermic process or an exothermic process? Justify your answer. c. Assume that the specific heat capacity of the calorimeter is negligible and that the specific heat capacity of the solution of urea and water is 4.2 J/ g oC throughout the experiment. i. Calculate the heat of dissolution for the solution made of urea AND water in joules. ii. Calculate the molar enthalpy of solution, Hosoln, of urea in kJ/ mo1 urea. 6. Reactions: Please write the unbalanced net ionic equation for each of the following: a. Calcium oxide is added to distilled water. b. Lead(II) nitrate solution is mixed with a solution of potassium iodide. c. Sulfurous acid is added to an excess solution of sodium hydroxide. d. Solid barium carbonate is strongly heated.