Chapter 8_part 1
advertisement

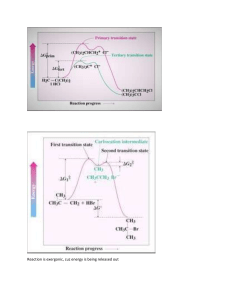
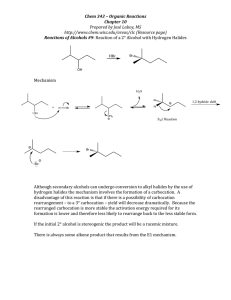
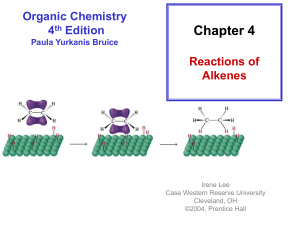
Alkenes and Alkynes II Addition Reactions Introduction: Additions to Alkenes An addition to a C-C double bond Electrophilic Addition Electrophilic Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes-Mechanism Electrophilic Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes Markovnikov’s Rule Example The Rate Determining step Step 1 is the rate determined step Formation of carbocation Theoretical Explanation of Markovnikov’s Rules Theoretical Explanation of Markovnikov’s Rules A mechanism for the reaction Predict the products and show the full mechanism Modern Statement of markovnikov’s Rule In the ionic addition of an unsymmetrical reagent to a double bond, the positive portion of the adding reagent attaches itself to a carbon of the double bond so as to yield the more stable carbocation as intermediate Regioselective Reactions When a reaction that can potentially yield two or more constutional isomers actually produces only one (or a predominance of one), the reaction is said to be regioselective HX + unsymetrical alkene more than product An exception of Markovnikov’s Rule When alkenes are treated with HBr in presence of peroxide, an anti-Markovnikov addition 8.3 Stereochemistry of the Ionic Addition to an Alkene The carbocation is formed in the first step of the addition is trigonal planar achiral 8.4 Addition of Sulfuric Acid Alkenes When alkenes are treated with cold concentrated sulfuric acid, they dissolve because they react with electrophilic addition to form alkyl hydrogen sulfate Alcohols from Alkyl Hydrogen Sulfate Alkyl hydrogen sulfates can be easily hydrolyzed to alcohols by heating them with water Markovnikov addition of H- and -OH example Provide mechanistic explanation for the following observation The addition of hydrogen chloride to 3-methyl-1-butene produces two products: 2-chloro-3-methylbutane and 2chloro-2-methylbutane Give the structure and name of the product that would be obatained from ionic addition of IBr to propene example In one industrial synthesis of ethanol, ethene is first dissolved in 95% sulfuric acid. In a second step of water is added and the mixture is heated. Out the reaction involved 8.5 Addition of Water to Alkene: Acid-Catalyzed Hydration Method for preparation of low molecular weight alcohols Usually regioselective Mechanism Rate determining step However, formation of 1o carbocation does not take place Rearrangement The carbocation formed initially invariable rearranges to a more stable one if possible Provide the full mechanism