Chapter 17 Review Answers 20. Metals 21. Allotropes 22. Metallic
advertisement

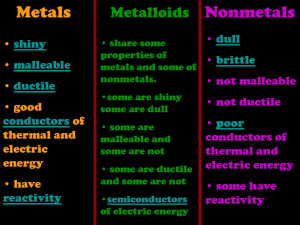
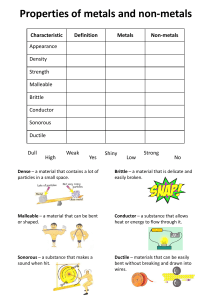
Chapter 17 Review Answers 20. Metals 21. Allotropes 22. Metallic bonding 23. Diatomic molecules 24. Transition elements 25. B 26. A 27. D 28. A 29. C 30. C 31. C 32. D 33. a. metals b & c transition elements, inner transition elements d & e hydrogen, noble gases 34. a. alkali b & c Cs, Na d. inner transition e. actinides f & g Hg, Fe 35. Lanthanides; europium, cerium, terbium Actinides; californium, nobelium uranium 36. Mercury might poison the person using the thermometer if it broke or leaked. 37. Hydrogen is flammable and, thus, dangerous. Helium is inert and nonflammable, so it is safer to use than hydrogen. 38. Nonmetals; they do not conduct electricity and are less malleable and ductile. 39. Silver compounds change chemically when they are exposed to light, and they leave an image on the paper. 40. All vitamin and pill bottles should have overdose warnings. They should clearly state that taking more than the recommended dosage could be harmful. 41. Aluminum is a metal because it is malleable, ductile, conductive, and shiny, and it can form ionic bonds with nonmetals. Also, a piece of aluminum contains metallic bonds – outer-level electrons are loosely held and shared between the Al atoms. Carbon is a nonmetal because it is not malleable, ductile, or shiny and because it is a poor conductor. It cannot form metallic bonds, but it can bond covalently with itself and other nonmetals. 42. Metallic bonding is a bond in which the outer-level electrons are loosely held and shared between all the atoms of the substance. This bond is why metals have the ability to conduct heat and electricity. 43. In a diamond, each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms at the corner points of a tetrahedron. Graphite consists of hexagonal layers of carbon atoms. The layers are weakly bonded to each other. The buckyball allotrope is a soccer-ball shaped molecule.