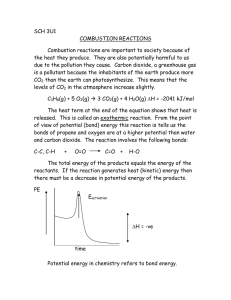
Classifying Reactions Types of Reactions Consider these reactions: CaCO3 (aq) CaO (aq) + CO2 (g) CO2 (g) + NaOH (aq) NaHCO3 (aq) a. How are these two reactions different? b. How would you describe, in words, what happens to the reactants in each case? Types of Reactions There are 6 categories of reactions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Synthesis (Combination) Decomposition Single Exchange Double Exchange Combustion Neutralization What is Synthesis (Combination)? Two elements are combined. A + B AB Example: H2 + I2 2 HI 2Fe + 3Cl2 2FeCl3 2SO2 + O2 2 SO3 What is Decomposition? A compound disintegrates or breaks down into more than one compound. AB A + B Example: 2H2O 2H2 + O2 Practice Classify the following reactions. Explain your reasoning. CaO + H2O Ca(OH)2 Combination 2Ag2O 4Ag + O2 Decomposition C12H22O11 12C + 11H2O Decomposition 2H2 + O2 2H2O Combination What is Single Exchange? One atom/ion trades places with another. A + BC AC + B Example: Zn + H2SO4 ZnSO4 + H2 Cl2 + 2KBr 2KCl + Br2 What is Double Exchange? Two atom/ions swap positions. AB + CD AD + BC Example: AgNO3 + NaCl AgCl + NaNO3 HCl + NaOH NaCl + H2O What is Combustion? A + oxygen B + C A is usually mainly composed of C and H. B and C usually include H2O or CO2. Example: CH4 + 4O2 CO2 + 2H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O Practice Classify the following reactions. Explain your reasoning. 3Na + FePO4 Fe + Na3PO4 Single Exchange ZnBr2 + 2AgNO3 Zn(NO3)2 + 2AgBr Double Exchange C3H8 + 5O2 4H2O + 3CO2 Combustion Pb(NO3)2 + K2CrO4 KNO3 + PbCrO4 Double Exchange