Chapter 2: How Cells Function
advertisement

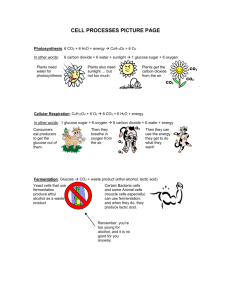
Have out your homework from yesterday On your own, without looking at your notes, see if you remember the next two steps of the levels of organization (before cell): Biosphere Ecosystem Community Population Organism Organ System Organ Tissue Cell Molecule Atom All matter in the universe, living and nonliving, van be broken down in to the basic substances called elements MOST matter exists a form made up of two or more elements joined together, known as a compound The smallest unit of any element is called an atom Most compounds in a cell are made up of atoms bonded together in molecules Water is a compound What are the elements that compose a water molecule? Hydrogen and Oxygen How many atoms of each element? H=2 O=1 What is another name for water? H2O Most activities that take place within a cell involve atoms and molecules interacting This is called a chemical reaction Bonds between atoms are broken and new bonds form to make different molecules Energy is needed to break bonds and energy is released when new bonds form ALL cells need a CONSTANT supply of energy All cells use chemical energy Energy stored in bonds between atoms of every molecule Must be able to release the chemical energy to stay alive Carbohydrates Simple carbs are sugars Provide the cell with energy Made from carbon, oxygen and hydrogen Major energy source for most cells is stored in glucose Sugar molecule Plants make sugars, animals have to eat plants Ultimate source of energy for almost all organisms is sunlight Plants change the energy in sunlight to a form of energy they can use– chemical energy in glucose What is the name of this process?? Why do people talk to their plants? Process done by plants to convert light energy into food The requirements for photosynthesis are: CO2 Sunlight Water Leaves Chloroplasts Root System Stomata Organelles of plant cells Capture light energy to conserve/store in form of ATP Chloroplasts trap light energy Obtains water from soil, travels through stem and to leaves Water enters leaf Microscopic pores on leaves of plant Act as gateway for efficient gas exchange Surrounded by guard cells that open and close the pore Carbon Dioxide enters leaf through Stomata DUE: Crossword Puzzle By yourself On a half sheet of paper What are the 3 things a plant requires from its external environment to complete photosynthesis What are the 3 main parts of a plant that are involved in photosynthesis Keep this piece of paper, we will need it at the end of the presentation Photosynthesis (Formula) Light Energy 6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H O 2 C6H12O6 + 6 O2 CO2 = __________ = What we breath out 6 _________ molecules 6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2 H2O= __________ 6 __________ water molecules Light Energy With light energy present, the product will be… 6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O C6H12O6 = ____________ = sugar = organic matter or food 2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2 O2 = __________ = what we breath in 6 ________ molecules A plant absorbs light energy from the sun and combines that with carbon dioxide from the air and water from the soil. This reaction creates sugar/glucose and oxygen The sugar/glucose is used as a food source for the plant The oxygen is put into the air for us to breath Why do people talk to their plants? Piece of paper Colored pencils Draw a model diagram of how Photosynthesis works Include: All the resources used, where the actions are done, what resources are produced and where they end up or how they are used. EVERYONE needs to be in their own assigned desk, studying (QUIETLY and on YOUR OWN) for the quiz today by the time the bell rings. Suggested studies: All of the terms we have covered this far in the photosynthesis notes I will be collecting your homework shortly after the quiz, and will be passing back your tests.