Classifying Chemical Reactions: Types & Examples
advertisement

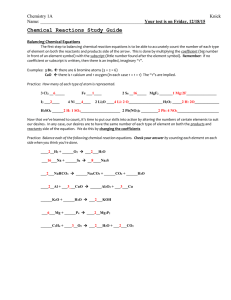
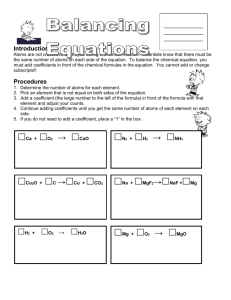
Classifying Chemical Reactions Reaction Types By classifying chemical reactions into several types, you can more easily predict what products are likely to form. Al + Fe2O3 → Fe + Al2O3 • Si Combustion Reactions • Is a the reaction of a carbon-based compound with oxygen. CH4(g) + O2(g) -> CO2(g) + H2O(l) C3H8(g) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(l) CH3CH2OH(l) + O2(g) → CO2 + H2O C(x)H(y) + O2(z) -> CO2 + H20 Synthesis Reactions • Mg(s) + O2(g) → MgO(s) • C + O2 → CO2 • A + B -> AB Decomposition Reactions • H2O(l) + -e -> H2(g) + O2(g) • H202 -> H20 + 02 • AB -> A + B Displacement Reactions • Cu(s) + AgNO3(aq) → Ag(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) Single displacement • Mg + Pb(NO3)2 → Pb + Mg(NO3)2 • A + BX -> B + AX Double-Displacement Reactions • HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → HOH(l) + NaCl(aq) • AX + BY -> AY + BX • • Balance each of the equations below, and indicate the type of reaction for each equation. a. Cl (g) + NaBr(aq) -> NaCl(aq) + Br (l) b. CaO(s) + H O(l) -> Ca(OH) (aq) c. Ca(ClO ) (s) -> CaCl (s) + O (g) d. AgNO (aq) + K SO (aq) ->Ag SO (s) + KNO (aq) 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 2 2 4 2 2 4 3 • Predict whether a reaction would occur when the materials indicated are brought together. For each reaction that would occur, complete and balance the equation. • a. Ag(s) + H O(l) • b. Mg(s) + Cu(NO ) (aq) • c. Al(s) + O (g) • d. H SO (aq) + KOH(aq) 2 3 2 2 4 2 • Predict the products, write a balanced equation, and identify the type of reaction for each of the following reactions. • a. HgO -> • b. C H OH + O -> • c. Zn + CuSO -> • d. BaCl + Na SO -> • e. Zn + F -> • f. C H + O -> 3 7 2 4 2 2 2 5 10 2 4