Unit D Chapter 2 Vocabulary
advertisement

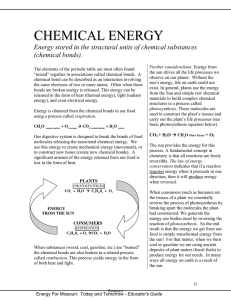
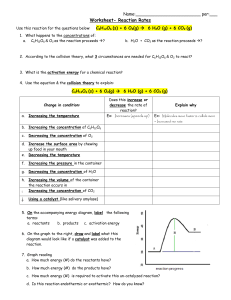
Unit D Chapter 3 Vocabulary 1. Chemical Reaction – the process by which chemical changes occur. Chemical bonds are broken, atoms rearrange themselves, and new bonds are formed. Ex. CH4 + 2O2 2H2O + CO2 2. Reactant – substance(s) present at the beginning of a chemical reaction. Ex. CH4 + O2 is burning natural gas. 3. Product – the result of a chemical reaction. Ex. H2O + CO2 after burning natural gas. 4. Precipitate – a solid product formed when two liquids react. Ex. Seashell. 5. Catalyst – a substance that changes another substance quickly without changing itself. 6. Law of Conservation of Mass – in a chemical reaction, atoms are neither created nor destroyed. 7. Coefficient – the number before a chemical formula that indicates how many molecules are involved in a chemical reaction. Ex. 2 O2 8. Concentration – amount of a substance contained in another substance at a given temperature. 9. Bond Energy – the energy associated with bonds. Breaking bonds requires energy and forming bonds releases energy. 10. Exothermic Reaction – a reaction in which energy is released. 11. Endothermic Reaction – a reaction in which energy is absorbed. 12. Photosynthesis – plants absorb sunlight and turn it into oxygen and glucose. Ex. H2O + CO2 C6H12O6 + O2 13. Respiration – reverse of photosynthesis. Ex. C6H12O6 + O2 H2O + CO2