Chemistry Elements & Periodic Table
advertisement
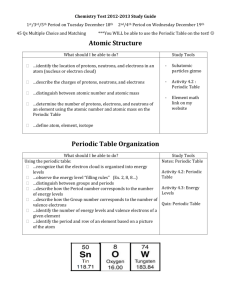
Non-metal, halogen family, atomic mass 35 • Chlorine 25 electrons, transition element Manganese • Gas, 48 neutrons Krypton • • Period 2, atomic mass 11 Boron Nonmetallic, period 3, atomic mass 32 Sulfur • 26 protons, period 4, transition element Iron • 12 neutrons, metallic, 11 electrons • Sodium 29 electrons, period 4 Copper • Atomic mass 20, gas Neon • • Period 5, transition element, 51 neutrons Zirconium 80 electrons, transition element Mercury • Period 4, lowest mass on periodic tables Potassium • Metallic, period 4, 20 electrons • Calcium Period 6, gas, 86 proton Radon • 4 neutrons, metallic Lithium • Period 4, metallic, 27 electrons • Cobalt Metallic, period 6, 56 protons Barium • Gas, atomic mass 16, 8 neutrons Oxygen • Mass less than 30, not neon, noble gas Helium • Period 5, metallic, 38 electrons Strontium • • Vertical columns in the period table • Families • Elements in families have similar _________ • Properties • Family of “salt-producing” elements like the non-metal in table salt • Halogens • Family in Group 18 on periodic table • Noble Gas • Horizontal rows on the periodic table • Periods • Each elements in a period is in a ______ group • Different • Elements on the left side of the periodic table • Metals • Elements on the ride side of the periodic table • Non-metals • Elements in Groups 3-12 on the periodic table • Transitions • Most widely used metal • Iron • Only liquid metal at room temperature • Mercury • Most abundant element in Earth’s crust • Aluminum • Odorless, tasteless, colorless gas; lightest of all elements • Hydrogen • Second most abundant element in Earth’s crust; found in glass and sand • Silicon • Gas element safe to use in balloons to make them float • Helium • Element contained in 80% of known compounds • Carbon