Chemistry Study Guide Words to know: Periodic Table Compounds
advertisement

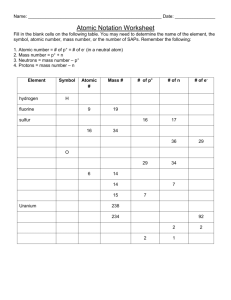
Chemistry Study Guide Words to know: Periodic Table Compounds Neutrons Melting Point Atomic Number Atomic Mass Atom Mixture Electrons Physical Properties Boiling Point Density Elements Protons Chemical Properties Precipitate Law of Conservation of Mass Matter Bond 1. Who is the creator of the modern Periodic Table? Dmitri Mendeleev 2. Elements are arranged in order of increasing __Atomic number___. 3. More than two thirds of the elements of the Periodic Table are _Metals_. 4. What atom has 37 protons and 37 electrons? Rb (Rubidium) 5. What is a compound? Groups of two or more elements that are bonded together example: NaCl (salt) 6. What is a mixture? Two or more elements or compounds combined together. Each of the substances can be separated from the group physically 7. Give an example of a chemical change (reaction). Milk goes sour, fry an egg, a nail rusts, hydrogen peroxide bubbles in a cut 8. Give an example of a physical change (reaction). Butter melts, aluminum foil is cut, water freezes 9. What does the atomic number tell us about the element? How many protons and electrons an element has. 10. What is a heterogeneous mixture? Substances are not evenly distributed (chocolate chip cookies, pizza) Chemistry Study Guide 11. What is a homogeneous mixture? Molecules are evenly spread throughout (aka solution) examples are air, blood 12. How many valence electrons does an atom need to have a full shell? 8 13. What elements had 4 protons, 5 neutrons, and 4 electrons? Be (Beryllium) 14. Periods in the Periodic Table run __horizontal__. (Horizontal or Vertical) 15. Groups or families in the Periodic Table run __Vertical__. (Horizontal or Vertical) 16. What is a precipitate? When 2 solutions are combined, they may form a solid substance. Indicates a chemical change has occurred 17. Define Melting point. The temperature at which a solid can change to a liquid 18. Define Boiling Point. The temperature at which a liquid boils 19. Define Density. Property that describes the relationship between mass of a material and its volume D=M/V 20. What is an element? The building blocks for all matter, describes atoms with specific characteristics 21. What are the 3 subatomic particles that make up an atom? Protons (positive charge), neutrons (no charge) and electrons (negative charge) 22. The number of protons is the same as the number of _electrons_. 23. How do you find the number of neutrons? Atomic mass – Atomic number = number of neutrons