Gene Action
advertisement

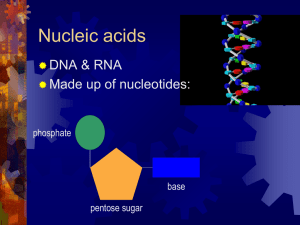
Gene Action Protein Synthesis Overview of Protein Synthesis … the short version DNA contained in genes provides instructions for making protein Information from a specific section of DNA is first transcribed to produce a specific molecule of RNA RNA attaches to a ribosome where the information is translated into a corresponding sequence of amino acids Protein Synthesis Vocab Nucleotide – building block of nucleic acid: sugar, phosphate, base Protein Synthesis Vocab Base Triplet – a sequence of three successive DNA nucleotides Codon – a sequence of three successive mRNA nucleotides that correspond with a base triplet TRANSCRIPTION DNA base triplets mRNA codons Just copying a message in the same language! – Nucleotide nucleotide Occurs in the Nucleus Catalyzed by the enzyme RNA polymerase – Promoter – a special sequence of DNA nucleotides near the beginning of a gene that tell the RNA polymerase where to begin reading TRANSCRIPTION Nucleotides pair complementarily: DNA C G A T - RNA G C U A TRANSCRIPTION Terminator – a specific sequence of DNA nucleotides that signals the end of the gene. RNA polymerase detaches from the RNA molecule and the DNA strand. The RNA leaves the nucleus through a nuclear pore Translation The process in which mRNA associates with ribosomes and directs the synthesis of proteins by converting the sequence on nucleotides in RNA to a sequence of amino acids…HUH? Changing Languages Now… – Nucleotide Amino Acids Translation http://staff.jccc.net/PDECELL/proteinsynth esis/translation/steps.html Translation 1. An mRNA molecule binds to the small ribosomal subunit and a special tRNA molecules (the initiator) binds to the start codon (AUG), where translation begins Translation 2. The large ribosomal subunit attaches to the small subunit, creating a functional ribosome – The initiator tRNA binds to the start codon – One end of the tRNA carries a specific amino acid, the other consists of a triplet of bases called an anticodon. – The anticodon pairs with the complementatry codon on mRNA Translation 3. The anticodon of another tRNA with its amino acid attaches to the next section of mRNA 4. A peptide bond is formed between the amino acids carried by the 2 tRNA’s Translation 5. After the peptide bond forms, the tRNA detaches from the ribosome and the ribosome shifts the mRNA strand by 1 codon. A new tRNA with amino acid binds to the exposed codon. Steps 3-5 repeat as the polypeptide lengthens Protein synthesis ends when the ribosome reaches a stop codon. – The new protein detaches, the tRNA detaches and the ribosome splits into its sub units How fast can this possibly happen? In the body translation occurs at a rate of about 15 amino acids per second! Before 1 ribosome finishes moving down the mRNA another can attach to that same strand allowing large amounts of protein to be built. tRNA