crassirostris
advertisement

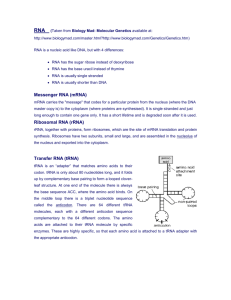
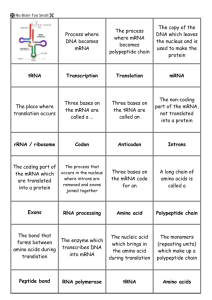
Watson & Crick Beedle & Tatum Processes: Transcription (DNA to mRNA) Translation (mRNA to protein) Importance of location Eukaryotes Prokaryotes Review Types of RNA in Gene Expression mRNA (messenger)-provides code for protein tRNA (transfer)-carries amino acids rRNA (ribosomal)-directs translation Requires DNA-dependent RNA Polymerase ▪ Core enzyme + sigma factor = holoenzyme Three forms in Eukaryotic Nuclei ▪ RNA Pol I –Pre-rRNA ▪ RNA Pol II**--Pre-mRNA ▪ RNA pol III –Pre-tRNA RNA recognizes region to be transcribed Promotor regions ▪ TATA box ▪ CAAT box Complementary mRNA produced from DNA Often zones with high GC levels Loop and release of mRNA Protection 5’ capped with 7-methyl G 3’ tail polyadenylation Prokaryotic cells translate immediately into protein Eukaryotic cells process mRNA before translation occurs Cutting out Introns Protecting transcript Splicing occurs by sequence snRNA and snRNP (spliceosomes), and/or ribozymes (self-splicing enzymes) Many different proteins can result from one transcript mRNA Transcript tRNA Carrier for amino acids Ribosomes Two sub-units of protein with three pieces of RNA Codons- 3 nucleotide codes for amino acids 20 amino acides 64 codons 3 stop codons (UGA, UAA, UAG) 1 Start codon (AUG-methionine) Each codon brings in a tRNA anti-codon that contributes one amino acid to the protein Small sub-unit of ribosome binds to mRNA Methionine “start” Large sub-unit of ribosome enters Initiation factors involved Connection Next tRNA enters 1st tRNA “hands” amino acid to 2nd tRNA, then leaves Ribosome slides to free the next space Continuation for length of protein Elongation factors involved Stop Codon is reached RF’s bind to stop codon Protein is released Ribosomal units disassociate Exploring factors influencing gene expression Expression and repression of genes Brooker, R. J. (2011). Concepts of Genetics + Connect Plus Access Card. McGraw-Hill Science Engineering, New York, NY. Brooker, R. J., (2012). Genetics: analysis and principles. 4th Ed. McGrawHill Higher Education, New York, NY. King, M. D. (2013). The Medical Biochemistry Page. Retrieved from: http://themedicalbiochemistrypage.org/home.html. McClean, P. E. (2013). Transcription. Retrieved from: http://www.ndsu.edu/pubweb/~mcclean/plsc731/transcript/transcript1.ht m Unknown (2013). Three types of RNA polymerase in eukaryotic nuclei. Retrieved from: http://mcb.berkeley.edu/courses/mcb110/ZHOU/lec.57.euk_trxn_apparatus.pdf Cap & Tail http://classconnection.s3.amazonaws.com/681/flashcards/894681/jpg/co ding1330783434942.jpg RNA Elongation http://limbiclab.files.wordpress.com/2012/12/limbic_lab_dna_transcripti on_diagram1.png RNA Initiation http://9e.devbio.com/images/ch05/0503fig1.gif Processing http://www.genomebc.ca/glossary/Alternative%20Splicing%20(colourful )_Image.gif Translation Initiation http://kvhs.nbed.nb.ca/gallant/biology/translation_initiation.jpg Translation Elongation http://kvhs.nbed.nb.ca/gallant/biology/translation_elongation.jpg Translation Termination http://utminers.utep.edu/rwebb/assets/images/17.17_Termination_of_tra nsla.jpg