Genetics Review KEY Phosphate Deoxyribose DNA: Color in the
advertisement
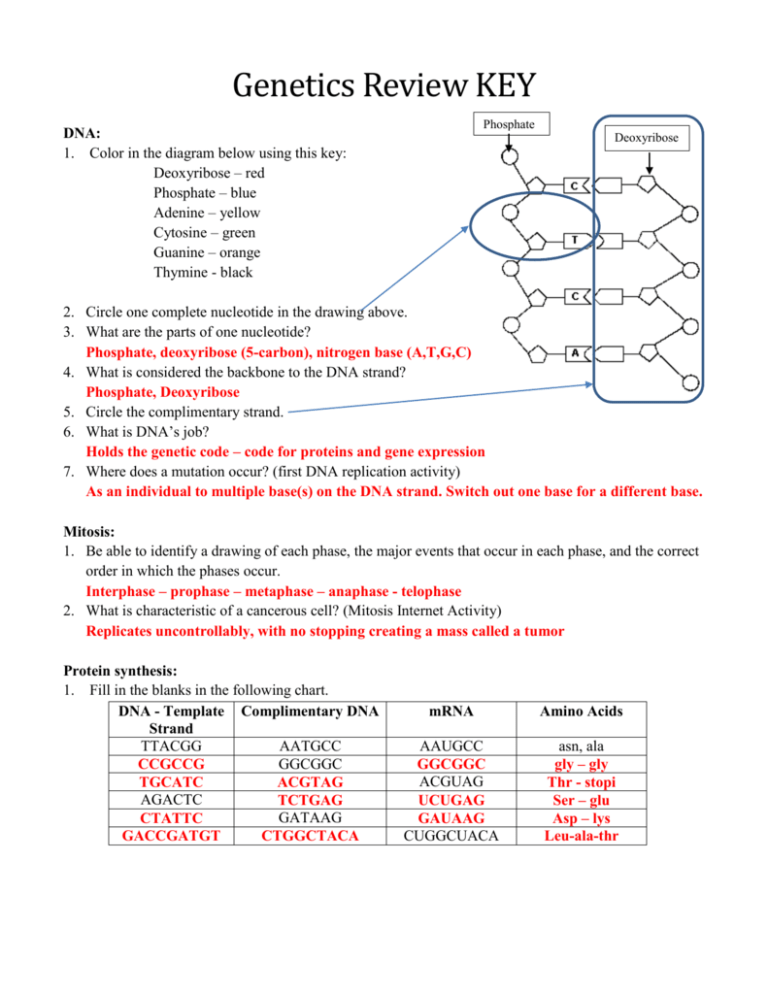
Genetics Review KEY Phosphate DNA: 1. Color in the diagram below using this key: Deoxyribose – red Phosphate – blue Adenine – yellow Cytosine – green Guanine – orange Thymine - black Deoxyribose 2. Circle one complete nucleotide in the drawing above. 3. What are the parts of one nucleotide? Phosphate, deoxyribose (5-carbon), nitrogen base (A,T,G,C) 4. What is considered the backbone to the DNA strand? Phosphate, Deoxyribose 5. Circle the complimentary strand. 6. What is DNA’s job? Holds the genetic code – code for proteins and gene expression 7. Where does a mutation occur? (first DNA replication activity) As an individual to multiple base(s) on the DNA strand. Switch out one base for a different base. Mitosis: 1. Be able to identify a drawing of each phase, the major events that occur in each phase, and the correct order in which the phases occur. Interphase – prophase – metaphase – anaphase - telophase 2. What is characteristic of a cancerous cell? (Mitosis Internet Activity) Replicates uncontrollably, with no stopping creating a mass called a tumor Protein synthesis: 1. Fill in the blanks in the following chart. DNA - Template Complimentary DNA Strand TTACGG AATGCC GGCGGC CCGCCG TGCATC ACGTAG AGACTC TCTGAG GATAAG CTATTC GACCGATGT CTGGCTACA mRNA Amino Acids AAUGCC GGCGGC ACGUAG UCUGAG GAUAAG CUGGCUACA asn, ala gly – gly Thr - stopi Ser – glu Asp – lys Leu-ala-thr Nucleus 2. Label the picture below using the following words: codon, anticodon, ribosome, nucleus, tRNA, mRNA, amino acid tRNA Amino Acid mRNA Codon Anti-codon Ribosome Codon 3. Distinguish between transcription and translation. Transcription occurs in the nuclues, an enzyme reads DNA into RNA and replaces T with a U Translation occurs in the cytoplasm, mRNA is read by the ribosome. It is read in triplets (codons) and the matching tRNA brings the appropriate amino acid to make a protein. 4. What is the job of the mRNA, ribosome, tRNA, rRNA, amino acid. mRNA – codes for protein ribosome – reads the mRNA tRNA – brings the amino acid to the ribosome rRNA – ribosomal RNA amino acid – monomer making up the polymer 5. How many amino acids are there? What codes for an amino acid? 20 Triplet codon on the mRNA 6. Fill in the table below: DNA 5-carbon sugar Deoxyribose Ribose Nucleotides ATGC AUGC Single or double stranded Double Single RNA Inheritance: 1. Define homozygous dominant Same dominant alleles expressed on the chromosome (two capital letters) 2. Define homozygous recessive Same recessive alleles expressed on the chromosome (two lower case letters) 3. Define heterozygous One dominant and one recessive allele on the chromosome (One capital and one lower case letter) 4. Define allele Different possible forms of the same gene 5. 6. Outline the process of meiosis (how is it different from mitosis)? Creates 4 haploid cells that are genetically different. It duplicates its DNA in interphase one, in Metaphase 1 the chromosomes line up as pairs (instead of a single line) at the equator. The pairs are separated in anaphase 1. Two haploid daughter cells are made. Each of those cells line their remaining chromosomes on the equator and split them so the result is 4 daughter cells with half of the genetic information. Buttercup flower color is determined by a gene with 2 alleles. Yellow (Y) is the dominant allele, and white (y) is the recessive allele. a. Draw a Punnett square for the cross between a homozygous recessive white flowered plant and a homozygous yellow flowered plant, providing the probability of each resulting phenotype and genotype. yy vs YY y y Y Yy Yy Y Yy Yy 100% Yy – heterozygous yellow b. Cross two children from the parent cross (one just did). Provide the probability of each resulting genotype and phenotype. Yy vs Yy Y y Y YY Yy y Yy yy 25% YY – homozygous dominant – yellow 50% Yy – heterozygous – yellow 25% yy – homozygous recessive – white











