Section: The Structure of DNA Read each question, and answer
advertisement

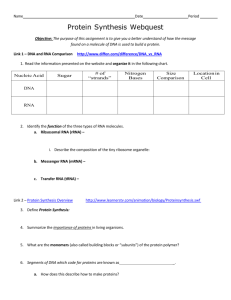
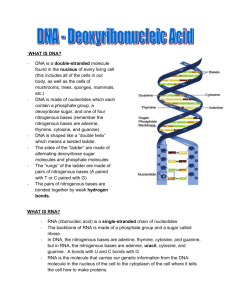
Section: The Structure of DNA Read each question, and answer based upon what you learn in the section. 1. Describe each research group’s contribution to the discovery of DNA’s role as the genetic material. a. Griffith b. Avery 2. Viruses that infect bacteria are called [bacteriophages / rough]. A virus is made of DNA and [proteins / cell walls]. Radioactive sulfur was used to label the [DNA / protein] in the viruses. Radioactive phosphorus was used to label the [DNA / protein] in the viruses. Hershey and Chase discovered that after the 32P-labeled phages infected the bacteria, most of the radioactive phosphorus was found in the layer containing [bacteria / phage]. 3. Hershey & Chase are given credit for discovering what? 4. Describe each research group’s contribution to the discovery of DNA’s structure. a. Chargaff: b. Franklin & Wilkins: c. Watson & Crick: 5. What is the “Central Dogma of Biology?” Match the letter of the phrase with the appropriate term 6. _____ double helix 7. _____ nucleotides 8. _____ deoxyribose 9. _____ hydrogen bond 10. _____ nitrogenous bases 11. _____ adenine 12. _____ cytosine a. a five-carbon sugar b. type of weak bond between base pairs that holds the double helix together c. four kinds and they form specific pairs d. subunits that make up DNA e. one of two pyrimidines used as a nitrogenous base in nucleotides f. one of two purines used as a nitrogenous base in nucleotides g. discovered that the amount of adenine always equaled the amount of cytosine and that guanine always equaled cytosine h. two strands of nucleotides twisted around each other 13. _____ Chargaff Describe each feature of DNA below 14. Complementary: 15. Anti-parallel: 16. Backbone: 17. Nucleotides: 18. Sketch & label the general shape of a nucleotide. 19. Purines: 20. Pyrimidines: 21. Hydrogen Bonds: 22. Base-pairing rules: 23. Practice: If a rattlesnake’s DNA was found to have 32% adenine, what is the % for each of the remaining bases? C%______________ G%______________ T%_______________ Section: Gene Expression, Transcription & translation Match the letter of the phrase with appropriate term 1. _____ribonucleic acid (RNA) a. the entire process by which genes are used to build proteins/traits. b. a molecule made of linked nucleotides 2. _____uracil c. the process of reading instructions on an RNA molecule to put together the 3. _____transcription amino acids that make up a protein 4. _____translation d. a 3-nucleotide sequence of mRNA e. the process of transferring a gene’s instructions for making a protein to an RNA 5. _____gene expression molecule 6. _____codon f. a nitrogenous base used in RNA instead of the base thymine found in DNA Complete each statement by identifying the correct term or phrase in the brackets. 7. Transcription begins when [RNA / RNA polymerase] binds to the gene’s promoter. The promoter region contains the sequence [AUG / TAC]. RNA polymerase adds complementary [DNA / RNA] nucleotides as it “reads” the gene. In eukaryotes, transcription takes place in the [nucleus / cytoplasm]. Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided. 8. What are three differences between RNA & DNA? 9. What determines where on the DNA molecule transcription begins and where it ends? Describe the role of each RNA molecule. 10. mRNA 11. tRNA 12. rRNA Complete each statement by identifying the correct term or phrase in the brackets. 13. Translation takes place in the [nucleus / cytoplasm]. It uses the molecules called [rRNA / tRNA] to bring [proteins / amino acids] to the [E.R. / ribosome] by matching their [anti-codon /codon] to the complementary [anti-codon / codon] in [DNA / mRNA]. 14. Study the following six steps in the synthesis of proteins. Determine the order in which the steps take place. Write the number of each step in order. _______a. The codon following the start codon then receives the tRNA molecule with the complementary anticodon. The tRNA carries the amino acid specified by the codon. _______b. Steps 2–5 are repeated until a stop codon is reached. The newly made protein is released into the cell. _______c. The first tRNA detaches, leaves behind its amino acid, and moves away from the ribosome. _______d. Enzymes help form a peptide bond between the amino acids of adjacent tRNA molecules. _______e. The tRNA (with its growing protein chain) and mRNA move one codon down, and the next codon is ready to receive the next tRNA and its amino acid. _______f. AUG. An mRNA, the ribosome, and a tRNA carrying the amino acid methionine bind together. The tRNA bonds to the “start” codon