CHAPTER 10 Study Guide Key (look up vocabulary in glossary or in
advertisement

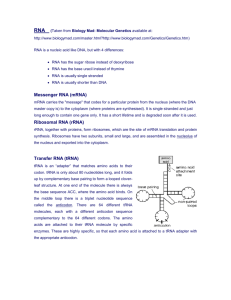
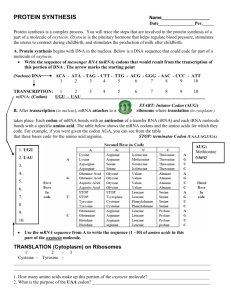
CHAPTER 10 Study Guide Key (look up vocabulary in glossary or in the chapter) 10-1 DNA MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. C D A B B SHORT ANSWER 1. The 3 parts of a nucleotide are a deoxyribose sugar + a phosphate + a nitrogen base (adenine, thymine, guanine or cytosine). These three components are held together with strong covalent bonds; the base pairs of the two strands are held together by weaker hydrogen bonds. 2. This is Chargaff’s rule, or the base-pairing rule. If 15% of a sample contains guanine, then 15% must be cytosine, since that is what guanine pairs with. This accounts for 30% of the sample; the remaining 70% is divided equally between the remaining base pairs (because of the base-pair rules), so divide by two and 35% is adenine and 35% is the thymine it pairs with 3. To make sure the offspring of the cell receives the exact same genes of the parent cell. 4. CRITICAL THINKING The hydrogen bonds connecting the base-pairs are easily broken so replication can occur. The stronger covalent bonds holding each nucleotide together maintains the integrity of the nucleotide sequences (ensures that the order doesn’t get mixed up, causing a mutation). STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS a) deoxyribose sugar 10-2 RNA MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5, C D A B D b) guanine c) adenine d) phosphate SHORT ANSWER 1. RNA contains ribose sugar instead of dexoyribose; RNA contains uracil, but not thymine; RNA is a single strand; RNA exists in both the nucleus AND the cytoplasm. 2. mRNA is a single, uncoiled strand; tRNA is a single chain coiled into a hairpin shape (also described as a cloverleaf); rRNA are the globular units in the cytoplasm 3. It is transcribed into mRNA in the nucleus, which then leaves through the nuclear pores. 4. CGAUUAGGC 5. CRITICAL THINKING RNA polymerase would not recognize the stop signal and would continue to synthesize RNA until a stop signal is reached. This would turn two separate genes into one gene. STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION The order of the steps (answers) are 3-1-5-2-4 10-3 Protein Synthesis MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. A D B C B SHORT ANSWER 1. UAC GUA CGU UCA AUC There would only by 4 amino acids in this polypeptide…every translation MUST end with a stop codon, in this case, AUC. Nothing is placed in the position of a stop codon, so the last one is not counted as an amino acid 2. The tRNA that pairs with the amino acid methionine is also the code for the start codon. 3. Proteins synthesized on the endoplasmic reticulum are exported from the cell; those synthesized on the free ribosomes remain within the cell. 4. CRITICAL THINKING All codons after the deletion would be shifted by one nucleotide, resulting in a completely different protein. STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS a) d) h) polypeptide/protein tRNA e) ribosome b) peptide bond c) amino acid anticodon f) codon g) mRNA