Click here to go back
advertisement
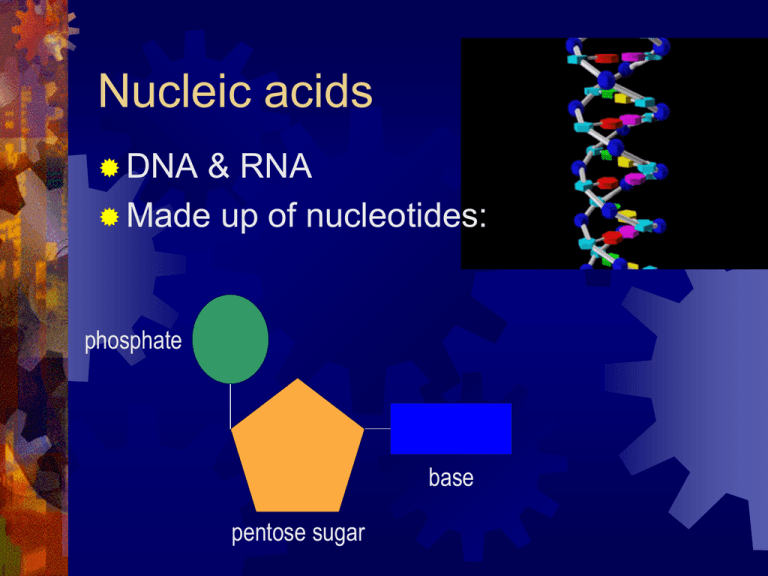
Nucleic acids DNA & RNA Made up of nucleotides: phosphate base pentose sugar Nucleotides 2 types of base: Pyrimidines - Cytosine C T Thymine Purines Adenine Guanine A G Complimentary base pairing Adenine will only bind with Thymine Cytosine will only bind with Guanine T A C G DNA structure nucleotide Condensation polymerisation of the deoxyribose nucleotides Replication—worksheet hw During cell division the DNA must replicate The enzyme helicase unwinds the DNA double helix The exposed bases bind to free floating nucleotides in the nucleoplasm DNA polymerase binds the complimentary nucleotides Replication is semiconservative The genetic code The sequence of nucleotide bases forms a code Each ‘code word’ has three letters– a triplet code Each codon codes for a specific amino acid e.g: GGG = proline CGG = glycine ATG = tyrosine ACT = stop (no amino acid) Protein synthesis The DNA codes for proteins A copy of DNA (mRNA) is made in the nucleus (transcription) The mRNA is used to make a protein (translation) in the cytoplasm Transcription Helicase unwinds the DNA Free nucleotides join onto complimentary bases RNA polymerase links adjacent nucleotides The completed mRNA moves out of the nucleus Transcription Three types of RNA Messenger RNA- made in the nucleus but sent to the ribosome mRNA Ribosomal RNA- makes up the ribosome (site of protein synthesis) with protein rRNA Transfer RNA-brings the appropriate amino acid to the ribosome for protein synthesis tRNA Translation mRNA binds to a ribosome tRNA carries an amino acid to the ribosome Amino acid activation transferRNA: tRNA binds onto a specific amino acid Translation A second tRNA brings another aa The two amino acids bind The process repeats Translation A polypeptide chain forms Eventually a stop codon is reached Acknowledgements . Animated cell models used by kind permission of The Virtual Cell website: Quiz a) b) c) d) 1. Which process involves tRNA: transciption translation DNA replication gene mutation Quiz a) b) c) d) 2. The formation of RNA does not involve: ribose sugar thymine removal of water phosphate








