Presentation Slides
advertisement

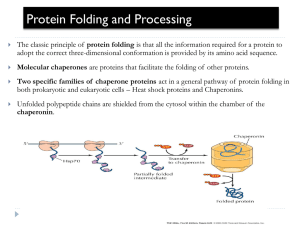
IDENTIFICATION OF CHEMICAL AND PHARMACOLOGICAL CHAPERONES TO TREAT ZSD PATIENTS WITH THE COMMON ALLELE, PEX1-GLY843ASP Gillian MacLean, Braverman Laboratory McGill University, Department of Human Genetics GFPD Family & Scientific Conference Lincoln, Nebraska July 28, 2013 OUTLINE Background Peroxisome matrix enzyme import Proteins and impact of genetic changes o PEX1 null and missense mutations Development of cell based assay Identification of drugs o chemical, pharmacological, combination therapies Future directions PEROXISOME BIOGENESIS DISORDERS Zellweger spectrum disorder (ZSD) (~1/60,000) Zellweger syndrome Neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy Infantile refsum disease Cannot assemble normal peroxisomes Multiple enzyme deficiencies Mutations in PEX genes lead to defects in PEX proteins Broad spectrum Can relate to which protein is affected and what the mutation is PEX PROTEINS ARE INVOLVED IN PEROXISOME MATRIX ENZYME IMPORT PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DEPENDS ON DNA SEQUENCE Proteins Polypeptides comprised of linked of amino acids Linear sequence gives rise to folded protein Sequence encoded by DNA Null allele = no protein produced Missense allele = different amino acid incorporated Nature Education, 2010 MOST ZSD MUTATIONS ARE ASSOCIATED WITH THE PEX1 GENE Encodes the PEX1 protein AAA ATPase (ATPase associated with diverse cellular activities) Uses energy from ATP to recycle PEX5 for additional rounds of import 60 % of all ZSD alleles 20% = PEX1-c.2097_2098insT (p.Ile700fs) (null) 20-30% = PEX1-c.2528G>A (p.Gly843Asp) (missense) PEX1-GLY843ASP (G843D) Missense allele Aspartate (D) Glycine (G) Misfolded protein Increased degradation Reduced function Non-native Mutation Unfolded protein However: Milder affect on patients Progressive Intermediate Arakawa et al. 2006 Native protein CELL BASED ASSAY DEVELOPED TO DETECT RECOVERY OF REPORTER PROTEIN IMPORTATION Patient fibroblasts grown in cell culture expresses “Green Fluorescent Protein” (GFP)-PTS1 reporter PEX1-G843D/null Courtesy of Joe Hacia FUNCTIONAL RECOVERY OF PEROXISOMES OBSERVED IN TREATED PEX1-G843D FIBROBLASTS Untreated 30 OC 200 mM TMAO GFP-PTS1 reporter localizes to the peroxisomes when: Grown at lower temperatures Grown with nonspecific chemical chaperones 100 mM betaine (Zhang et al., 2010) FUNCTIONAL RECOVERY SUGGESTS IMPROVED FOLDING Decrease temperature Cells are in lower energy state Reduced degradation of misfolded proteins Proteins have more time to find correct conformation Not applicable for patients Chemical chaperones Create environment for better protein folding Non- specifically enhances protein folding Requires high concentrations ASSAY EFFECTIVELY USED FOR THE IDENTIFICATION OF POTENTIAL DRUGS Screened 2000 small molecule compounds Identified hit compounds flavonoids No treatment (- ) 10 uM Diosmetin 150 mM Betaine(+) TESTING OF ADDITIONAL FLAVONOIDS Tested >50 flavonoids Compared import recovery by dose response 2,5, and blinded comb % Importing Cells 100 Diosmetin Acacetin Ac. diacetate Apigenin Kaempferol Chrysin Galangin Tamarixitin 80 60 40 20 0 0 10 20 Concentration (M) 30 DISCOVERY OF POTENTIAL PHARMACOLOGICAL CHAPERONES Pharmacological chaperones: Interact with proteins selectively -> stabilize or improve folding May be, or mimic binding partners Enzyme substrate Protein ligand Co-factors PEX1 is a AAA ATPase Flavonoids bind ATP bining sites POTENTIAL FOR COMBINATION THERAPIES Chemical chaperones: Interact with proteins non-selectively Betaine Pharmacological chaperones: improve PEX1-G843D folding Interact with proteins selectively Flavonoids Proteasome inhibitors: Inhibit degradation of misfolded proteins Bortezomib PEX1-G843D levels COMBINATION THERAPIES RESULT IN AN ADDITIVE EFFECT Low doses betaine + flavonoid = more effective than high dose flavonoid CONFIRMATION OF CELL-BASED REPORTER ASSAY Evaluate recovery of endogenous matrix enzyme import Evaluate biochemical parameters Plasmalogen levels DHA levels SUMMARY AND FUTURE DIRECTIONS Effective cell based assay PEX1-G843D patient cell line GFP-PTS1 reporter Demonstrates recovery Chemical and pharmacological chaperones identified Shown to work in combination Better understand current potential compounds Develop more sensitive, more general assays Continue to look for even better compounds Treat a broader group of patients ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Nancy Braverman laboratory Catherine Argyriou Sara Birjandian and Tara Saberian Sarn Jiralerspong Erminia Di Pietro Claudia Matos-Miranda Wei Cui Steve Steinberg and Shandi Hiebler Joe Hacia Gabrielle Dodt McGill community Eric Shoubridge and Olga Zurita Armando Jardim Murielle Akpa A special thanks to families and patients for their kind contributions FUNDING ORGANIZATIONS Woodbury Peroxisome Disease Family Funding