Synthesis of Novel Flavonoids by Combination of Plant Flavonoids
advertisement

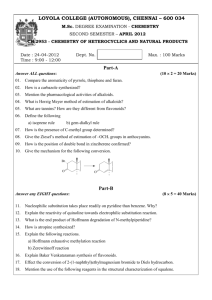
Example Synthesis of Novel Flavonoids by Combination of Plant Flavonoids and Microbial Glycosides Tae Jin Oh and Jae Kyung Sohng Department of Pharmaceutical Engineering, Institute of Biomolecule Reconstruction, Sun Moon University, Asansi, Chungnam, 336-708, Korea E-mail: sohng@sunmoon.ac.kr, Tel:82-41-530-2246, Fax: 82-41-544-2919 Flavonoids comprise a large group of low molecular weight polyphenolic secondary plant metabolites. It is important natural pharmaceutical compounds found showing antioxidant, antibacterial and anti-viral activities as well as anti-allergic effects, and possess antiinflammatory, anti-angiogenic, analgesic, hepatoprotective, cytostatic, apoptotic estrogenic or anti-estrogenic properties. Biosynthesis of glycosylated natural compound results in the formation of an overwhelming number of natural glycosides with numerous applications like solubility, stabilization and detoxification . The engineered E. coli BL21(DE3, △pgi) cells generated by deleting the glucose-phosphate isomerase (pgi) gene and heterologously expressing TDP-deoxysugar, TDP- aminodeoxysugar and glycosyltransferase genes from various sources were used as whole cell biotransformation reaction by feeding exogeneously. To generate glycosylated flavonoids, the engineered E. coli cells were fed with quercetin, keampferol and fisetin, the flavonol (or 3-hydroxyflavone) exogenously. flavonoids, 3-O-deoxyallose The products were analyzed to be 3-O-rhamnosylflavonoids, 7-O-glucuronyl flavonoids and 3-O- aminodeoxysugar flavonoids. Since the deoxysugar glycosylated flavonoids increase antibacterial activity and have shown enormous pharmaceutical properties, the recombinant host generated can be utilize to discover unusual glycosylated flavonoids as functional materials and drugs. Acknowledgment This work was supported by a grant from the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (SSAC, grant#: PJ008013), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.