Cell Cycle 1
advertisement

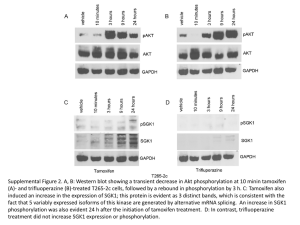
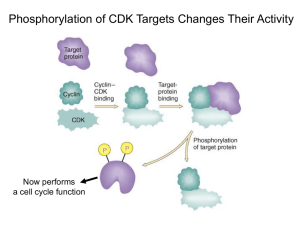
The cell cycle chromosome duplication S G1 G2 M cell division (cytokinesis) nuclear division (mitosis) The cell-cycle control system metaphaseanaphase transition G2/M transition M G2 S Start transition G1 The heart of the cell cycle control system: Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) Cdk Cyclin Basic framework of the cell-cycle control system Yeast: Cln1, 2 Clb5, 6 Clb2 Vertebrate: Cyclin E Cyclin A Cyclin B Order - Completeness - Irreversibility - Robustness - Regulatability Cdk1 has hundreds of targets in the cell Cdk1 phosphorylation sites often cluster in disordered loops and termini Site A Site B Predicted disorder Quipu Phosphorylation is like Quipu P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P …how is the pattern generated, and how is it decoded? Cyclin-specific Cdk1 substrates contain motifs that interact with a docking site on the cyclin Cyclin Cdk Active site of Cdk ‘Hydrophobic patch’ on cyclin S/T*-P-x-K/R R-x-L phosphorylation site on substrate motif on substrate The Cks1 subunit provides an additional docking site for pre-phosphorylated sites substrate Turning on S-Cdk in budding yeast Start The switch at G1/S: textbook dogma Phosphorylation of Sic1 by Cdk1 triggers its destruction via the ubiquitin ligase SCFCdc4 Ub Ub Ub Cdc4 E2 Ubiquitin SCFCdc4 Rbx1 Cul1 Skp1 Sic1 is loaded with Cdk phosphorylation sites that drive binding to the Cdc4 subunit of SCF Cdc4 E2 Ubiquitin SCFCdc4 Rbx1 Cul1 Skp1 Structure of an ideal phospho-peptide binding to the Cdc4 subunit of SCF The optimal Cdc4-binding site (‘CPD’): L/I-L/I/P-pT-P-[R/K]-[R/K]-[R/K]-[R/K] disfavored Nash et al. (2001) Nature 414:514-21. Orlicky et al. (2003) Cell 112:243-256. But the Cdc4-binding sites in Sic1 are pretty bad…why? Optimal Cdc4-binding site (‘CPD’): L/I-L/I/P-pT-P-[R/K]-[R/K]-[R/K]-[R/K] Suboptimal Cdc4-binding sites in Sic1: Nash et al. (2001) Nature 414:514-21. Binding to SCFCdc4 requires six sites of phosphorylation on Sic1 Phospho-Sic1 binding to Cdc4 Nash et al. (2001) Nature 414:514-21. Six suboptimal sites somehow lead to high affinity? Sic1 Cdc4 Cdc4 Cdc4 The model: distributive phosphorylation of Sic1 on six sites leads to ultrasensitive Clb5-Cdk1 activation at G1/S The model: distributive phosphorylation of Sic1 on six sites leads to ultrasensitive Clb5-Cdk1 activation at G1/S The first fly in the ointment: a second phosphate binding site on Cdc4 Cdc4 Cyclin E peptide Hao et al. (2007) Mol. Cell 26:131-143. Two or three good di-phosphodegrons in Sic1 7 mM 3 mM Hao et al. (2007) Mol. Cell 26:131-143. The latest complication: processive phosphorylation of Sic1 in vitro PhosphoSic1 (Phos-Tag gels) Kõivomägi et al. Nature 480, 128 (2011). Processive phosphorylation depends on the Cks1 subunit substrate Kõivomägi et al. Nature 480, 128 (2011). Phosphorylation by Clb5-Cdk gets a boost from a docking site Clb5 hydrophobic patch mutant Clb5 RXL mut substrate Kõivomägi et al. Nature 480, 128 (2011). Cascades of phosphorylation drive Sic1 degradation: Cln-Cdk1 starts things out with the help of a docking site P P P P P Kõivomägi et al. Nature 480, 128 (2011). Clb5-Cdk1 takes it the rest of the way P P P P P P P Kõivomägi et al. Nature 480, 128 (2011). Cascades of phosphorylation events drive Sic1 degradation: mystery solved! P P P P P P P Kõivomägi et al. Nature 480, 128 (2011). The switch at G1/S depends on positive feedback The central problem of mitosis ? one nucleus containing duplicated chromosomes two nuclei, each with one set of chromosomes The solution: biorientation of sister chromatids on a bipolar spindle sister chromatid pair kinetochore spindle pole A thing of beauty is a joy forever Prophase Prometaphase Anaphase A Anaphase B Metaphase Telophase How sister chromatid pairs are attached: the ‘search and capture’ model