Stakeholder analysis of urban pluvial flood risk management
advertisement

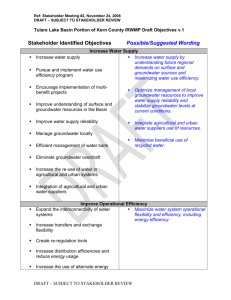
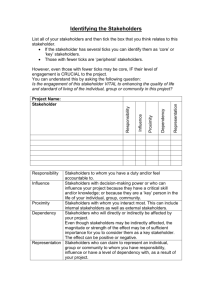
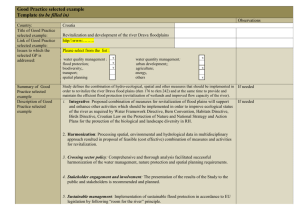
SANAA OSMANI Centre for Environmental Policy Imperial College London MSC PROJE CT 2010 Identify all stakeholders (esp. Local champions) Categorise stakeholders Understand stakeholders’ issues Establish any relationships/ interactions between the stakeholders River Roding Source: Environment Agency (2010) Legislative Drivers ◦ 2010 UK Flood and Water Management Act ◦ 2007 EU Floods Directive ◦ 2008 EU Water Framework Directive ◦ 2008 Pitt Review recommendations ◦ Aarhus Convention Principles Feeds into the aims of the DIANE-CM project of enhancing the capacity of stakeholders to cope with flood risk and increase resilience Stakeholder analysis (SA) will evaluate the current level of flood risk awareness amongst stakeholders Identify key champion stakeholders who are most likely to facilitate FRM strategies Initial stage in increasing public participation in environmental decision-making Improving risk communication and hazard awareness by identifying any barriers Revealing Governance networks Brainstorming session with 4 key stakeholders Triangulation Confirm findings from interviews Stratified systemantic random sample of property owners in high flood risk areas snowballing Semi-structured interviews Questionnaire surveys Second round of interviews? Time constraints Factist discourse analysis on interview transcripts Statistical analyses on quantitative data from questionnaire surveys Power-influence and interestinfluence matrices Stakeholder map/ Sociogram showing linkages and interactions An assessment of stakeholders’ flood risk awareness Identification of barriers to stakeholder participation Relationships between different stakeholders The results of this research will be used in later stages of the DIANE-CM Project when evaluating the effectiveness of stakeholder involvement SA should establish a platform facilitating stakeholder interaction and learning to reach a consensus