Stakeholder Analysis Support (SAS) tool
advertisement

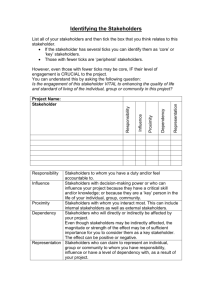
Supporting Actor Analysis using the I3S: Stakeholder analysis support (SAS) tool What is actor analysis? … a way to understand who is affected by and who has the power to influence water policy decisions and implementation, i.e. the stakeholders Why perform stakeholder analysis? Three theoretical approaches: •To understand who’s in and why (descriptive approach) •Influence and manage stakeholder relationships (instrumental approach) •Legitimise stakeholder involvement and empowerment in decision-making processes, and to ensure representation of under-represented or marginalised groups (normative approach) Why perform stakeholder analysis? so.. make sure all relevantof …to facilitate the processes stakeholders are or involved or your social, economic environmental project might fail change and adaptation Steps in actor analysis Context Identify focus (e.g. issue, organisation or intervention) High level cognitive mapping using C-map tools Identify system boundaries Application of stakeholder methods Identify stakeholders and their stake Differentiate between and categorise stakeholders Stakeholder Analysis Support (SAS) tool Investigate relationships between stakeholders Actions Recommend future activities and stakeholder engagement Detailed mapping of cause-effect relationships between stakeholders and the subsequent impact on environmental indicators using knowledge maps, influence diagrams, and quantification using Bayesian belief networks Context for testing Follow the link to actor analysis scenario in the I3s workshop website Interest functions • Regulation: e.g. flood water storage, drainage. • Habitat: e.g. for wildlife, important for conservation organisations • Information: e.g., providing education to citizens (amenity), research value to NGOs (landscape) • Production: e.g. drinking water abstraction, industrial production, agricultural production • Carrier: e.g. transport, industrial sites, settlements High INTEREST Subjects: •high interest but low influence Key players are stakeholders •theywho are supportive, but lack the capacity for should to be actively groomed, because impact, they have high interest in and•they influence may become influential by forming over a particular phenomenon. alliances with other stakeholders •often the marginal stakeholders Subjects Key players that development projects seek to empower Context setters are highly influential, The Crowd are stakeholders who have little but have little interest. Because of interest in or influence over desired outcomes this, they may be a significant risk, and there is little need to consider them in and should be monitored and much detail or to engage with them. managed. Context setters Low Crowd Low INFLUENCE High How can results from the SAS tool be used to facilitate engagement, policy implementation and the process of change? • Provides a structured approach to investigating existing and potential collaborative relationships between stakeholders, and the barriers to and drivers of these relationships • Identify which actors are currently considered key to the collaborative effort and why. Some are important financial supporters, other possess essential knowledge, whilst others still may have already recognised appropriate linkages and shared interests upon which further collaboration may be built. • Representation of under-represented or marginalised groups - Finally, it allows us to consider which stakeholders are bypassed and how including them may benefit other stakeholders, along with how such input may affect existing management objectives. Evaluation questionnaire