18-3 Kingdoms and Domains
advertisement

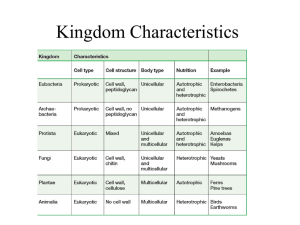
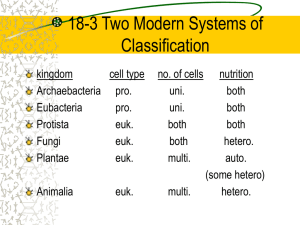
18-3 Kingdoms and Domains The Tree of Life Evolves Organisms originally grouped as either plant or animal Scientists realized that bacteria, protists and fungi were quite different from plant and animal groupings Tree of Life Evolves Bacteria and protists were placed in the kingdom Protista Fungus, yeasts and molds placed in kingdom Fungi Tree of Life Evolves Realized bacteria lacked nuclei and organelles Regrouped into kingdom Monera Tree of Life Evolves This process lead to 5 kingdoms: – Monera – Protista – Fungi – Plantae – Animalia Tree of Life Evolves In recent years, it has been discovered that bacteria fit into 2 distinct categories Monera has been broken into: – Archaebacteria (ancient bacteria) – Eubacteria (new bacteria The Three Domain System Domain is a more inclusive category than kingdom Three domains: – Eukarya: includes protists, fungi, plants, and animals – Bacteria: includes kingdom Eubacteria – Archaea: includes kingdom Archaebacteria Domain Bacteria Members of domain bacteria are unicellular and prokaryotic Have thick, rigid cell walls around cell membrane Cell wall contains peptidoglycan Domain Bacteria Ecologically diverse – free-living soil organisms to deadly parasites Some photosynthesize others don’t Some need oxygen, others killed by it Domain Archaea Unicellular and prokaryotic Live in most extreme environments – Hot springs, brine pools, and black organic mud Many only live in anaerobic environments Cell walls lack peptidoglycan Domain Eukarya Consists nucleus of all organisms that have a Composed – Protista – Fungi – Plantae – Animalia of kingdoms: Protista Eukaryotic organisms that can’t be classified as plant, animal, or fungi Members Most algae have great variety are single-celled, multicellular Protista Photosynthetic Some or heterotrophic have characteristics of fungi – Others characteristics of plants – Others characteristics of animals Examples: amoeba, paramecium Fungi Heterotrophs Feed on dead or decaying organic matter Secrete digestive enzymes into food, and absorb molecules through bodies Multicellular (mushrooms) and unicellular (yeasts) Plantae Multicellular Photosynthetic autotrophs Nonmotile (don’t move) Cell walls that contain cellulose Contains cone-bearing and flowering plants, mosses and ferns Animalia Multicellular and heterotrophic Do not have cell walls Most can move about for at least part of their life cycle Great diversity, live in nearly every part of planet