PRIMITIVE EARTH had no oxygen
advertisement

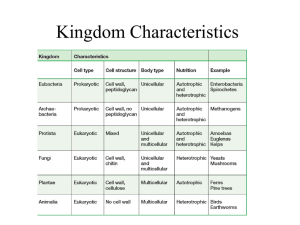
PRIMITIVE EARTH had no oxygen THE RELATIVE SIZES OF LIVING THINGS DNA ties all Kingdoms together ------E u k a r y o t e s---- Evolution with 5 Kingdoms Biodiversity Is a Crucial Part of the Earth’s Natural Capital • • • • • Vital renewable resource Species diversity Ecosystem diversity Functional diversity The biodiversity found in the earth’s genes, species, ecosystems, and ecosystem processes is vital to sustaining life on earth. How Do Speciation, Extinction, and Human Activities Affect Biodiversity? • As environmental conditions change, the balance between formation of new species and extinction of existing species determines the earth’s biodiversity. KINGDOM MONERA =PROKARYOTES = bacteria Characteristics: • Tiny cells (1-10 um = microns) • complex cell wall • unicellular, • no nucleus, no organelles KINGDOM MONERA = PROKARYOTES = bacteria Characteristics: •For food = Eat “stuff” or decomposers or photosynthetic • Anaerobic (live without oxygen) or Aerobic (can live with oxygen) CYANOBACTERIA: Likely the 1st photosynthetic Organisms (make O2) and are responsible for our Oxygen atmosphere. Bacteria are tiny = 1-10 um (microns) BACTERIA ON THE HEAD OF A PIN Symbiotic bacteria in legume roots provide Nitrogen to Plants The bacterium "communicates" with the host plant and that leads to a symbiotic partnership. The bacterium will attach to root hairs and release compounds that cause the roothairs to curl. bacterium Escherichia coli Inside a cows stomach region, there are 4 digestive departments About 100 strains of E. coli are common in animal intestines – and mostly beneficial. Some produce Vitamin K2, while others fight harmful intestinal bacteria. The dangerous strain is quite rare, Escherichia coli O157:H7, discovered in 1982, and can cause bloody stools, abdominal cramps, and even death via kidney failure. It’s totally safe to the original host animal (cows, sheep, chickens, etc). SOME BACTERIUM HAVE DRUG RESISTANCE BECAUSE OF ANTIBIOTICS OVERUSED ON LIVESTOCK A strain of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteria that humans was originally a human strain. http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2012-02/asfm-mil021612.php Nationwide study finds U.S. meat + poultry is widely contaminated Multi-drug-resistant Staph found in nearly 1 in 4 samples. April 15, 2011 — Drug-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus, a bacteria linked to a wide range of human diseases, are present in meat and poultry in stores across the US. In 136 samples of beef, chicken, pork and turkey of 80 different brands, 47% were contaminated by S. aureus and 52% of those were resistant to "at least 3 classes of antibiotics" and as high as 9 (Journal of Clinical Infectious Diseases). http://www.tgen.org/news/index.cfm?pageid=57&newsid=1948 KINGDOM PROTISA Characteristics: *Unicellular Eukaryotes *Protozoa + algae *maybe cell wall *eat “stuff” and/or photosynthetic size = 10 - 100um Paramecium protozoa cell with cilia Kelp – a brown algae is a Protista Hydra. This small aquatic animal is green because of the numerous green algal cells living symbiotically within its tissues. Diatoms are Protista Red Tides are caused by a marine dinoflagellate, a Protista ! Characteristics: *Eukaryotes *multicellular (except yeast) *cell walls of chitin *decomposers KINGDOM FUNGI Bread mold sporangium Yeast cells are single-celled Fungi that make beer alcoholic and bread rise Lichens : a symbiotic relationship between 2 kingdoms (a Protista and a Fungus) A “Mycorrhizal” symbiotic fungi helps a conifer grow better by fixing nitrogen NO YES WHO WERE THE FIRST FARMERS? Over 50 million years of evolution, leafcutter ants in central america have evolved a mutualism where ants are successful farmers growing huge underground fungus gardens which are the only source of nutrition for huge colonies with millions of ants. http://www.news.wisc.edu/18956 / Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi + Plant Symbiosis AM fungi have symbiotic associations with almost 80% of plants, mainly herbaceous ones, including cultivated crops that feed the world (cereal crops, market garden products, Field culture of mycorrhizal leek fruits and vegetables). plants http://www4.agr.gc.ca/AAFC-AAC/display-afficher.do?id=1236712919454&lang=eng KINGDOM - PLANTS Characteristics: •Eukaryotes •cell wall of cellulose •photosynthetic a. Moss b. Club Moss D. Gymnosperm = Conifers c. Fern E. Angiosperm = Flowers Diversity of the Plant Kingdom Moss Club Moss Fern Conifers + cycads + Flowering Plants Mosses are primitive land plants that reproduce with spores Horsetails are primitive land plants Strawberry’s have seeds + belong to the Rose family, which include apples, pears, blackberries and other foods. This monstrous flower has what for pollinators? KINGDOM ANIMALS • Multicellular • Eukaryotes • No cell walls • “eat stuff” ANIMALS without backbones = Invertebrates We can compare genes coding for blood Hemoglobin to build evolutionary lines. Adaptive Radiation = splitting of a lineage to form many species with different ecological niches 145-251 MYA 65 MYA to Present MYA = million years ago Continental Drift affected species movement and diversity Fig. 5–6 © Brooks/Cole Publishing Company / ITP Plants and Animals evolved through interactions Bees + other insects provide over $150 billion worth of pollination to farmers worldwide every year. Soils are rich and diverse Ecosystems Soil is a complex living food web, where organisms interact to process organic matter, recycle nutrients, and nurture plants. Although we may not see all of them in action, microorganisms and invertebrates make enormous contributions to food and agriculture. They pollinate plants, recycle nutrients in soils, ferment bread and cheese, help animals digest forage, and provide natural protection against plant pests. Hey! Who are you callin’ an Animal ?!? aquatic fungiAllomyces