Pharmacotherapy
advertisement

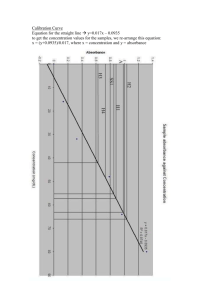
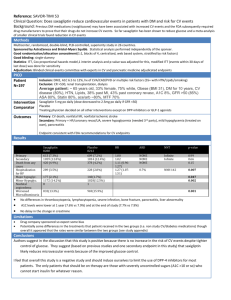
Pharmacotherapy • Oral Hypoglycemic Agents (OHA) • Antihyperglycemic agents • Used only in type 2 diabetes, with diet and exercise • CDA Clinical Practice Guidelines “Pharmacologic Management of Type 2 Diabetes, p S53 Pharmacotherapy Class: Biguanides (Insulin Sensitizer) Generic Brand Advantages Disadvantages Metformin Glucophage, Glumetza -Weight neutral -GI side effects -low risk of (nausea, bloating, hypoglycemia diarrhea, decreased appetite) A1C ↓ 1-2% Mechanism of Action: ↓ hepatic glucose production and intestinal glucose absorption, ↑glucose uptake and insulin sensitivity, lowers basal and post-prandial blood glucose levels Comments: -first line agent in type 2 -good as initial therapy especially if overweight -best to gradually increase dose to ↓ GI side effects -Contraindicated if CrCl/eGFR <30 mL/min or hepatic failure -Caution with renal insufficiency (eGFR<30ml/min) -lactic acidosis may be precipitated by renal impairment, excessive alcohol intake, hepatic disease, acute CHF Pharmacotherapy Class: Sulfonylureas and Meglitinides (Insulin Secretagogues) Generic Brand Advantages Disadvantages A1C ↓ Glyburide* Diabeta -rapid effect 1-2% Gliclazide Diamicron -weight gain, risk of hypoglycemia, dizziness, headache, nausea, weakness Glimepiride Amaryl Repaglinide Gluconorm -expensive Mechanism of Action: Stimulates functional β cells in pancreas to release insulin, ↓ glucose output from liver Comments: -take with food -hypoglycemia and weight gain are especially common with glyburide* -caution with patients at high risk of hypoglycemia (e.g. the elderly, renal/hepatic failure) Pharmacotherapy Class: Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors Generic Brand Advantages Acarbose Glucobay -Weight neutral -GI side effects -low risk of (diarrhea, gas, hypoglycemia cramps, liver dysfunction) Prandase Disadvantages A1C ↓ 0.5-0.75 % Mechanism of Action: Delays digestion of CHO and gastrointestinal absorbtion of glucose. Inhibits pancreatic amylase and membrane bound intestinal α-glucoside hydrolase. Comments: -Take with food (first bite of meal) -Takes up to 8 weeks for maximum efffect -Not recommended as initial therapy in people with marked hyperglycemia (A1C >9.0%) Pharmacotherapy Class: Tiazolidinidediones (TZD) or Glitazones (Insulin sensitizers) Generic Brand Advantages Disadvantages A1C ↓ Pioglitazone Actos Rosiglitazone Avandia -improved lipid profile, low risk of hypoglycemia, potential decrease in MI (pio) -Slow onset, fluid retention, weight gain, bone fractures, expensive, potential increase in MI (rosi) 0.5-2% Mechanism of Action: ↓ insulin resistance, improves target cell response to insulin, ↓ hepatic glucose production Comments: -may induce ovulation -only covered by blue cross through special authorization –must be intolerant to metformin -take at same time everyday -some blood pressure lowering Pharmacotherapy Class: Glucacon Like Peptide 1 (GLP-1) (Incretins) Generic Brand Advantages Disadvantages A1C ↓ Liraglutide Victoza Exenatide Byetta -weight loss, low risk of hypoglycemia -injection, expensive, 0.5-1.5% long-term safety not established, GI side effects Mechanism of Action: Glucagon Like Peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists act to ↑ insulin release in the presence of ↑ glucose, ↓ glucagon secretion and delay gastric emptying Comments: -may be beneficial for weight loss -may delay gastric emptying and impact absorption of oral meds (caution with antibiotics and contraceptives) -caution with patients at high risk of hypoglycemia (e.g. the elderly, renal/hepatic failure) Pharmacotherapy Class: Dipeptidylpeptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors (Incretin) Generic Brand Advantages Disadvantages Sitagliptin Januvia Saxagliptin Onglyza -weight neutral, -expensive, longlow risk of term safety not hypoglycemia established A1C ↓ 0.5-0.75% Mechanism of Action: DPP-4 is an enzyme that breaks down the incretin hormones GIP and GLP-1 to help increase the release of insulin and decrease glucagon levels in the circulation Comments: -Better post prandial glucose control Pharmacotherapy Insulin • Rapid Acting – Humalog (lispro) • Short Acting – Humulin R – Novolin • Intermediate Acting – Humulin N • Long Acting – Lantus – Levemir