Ch.6mod
advertisement
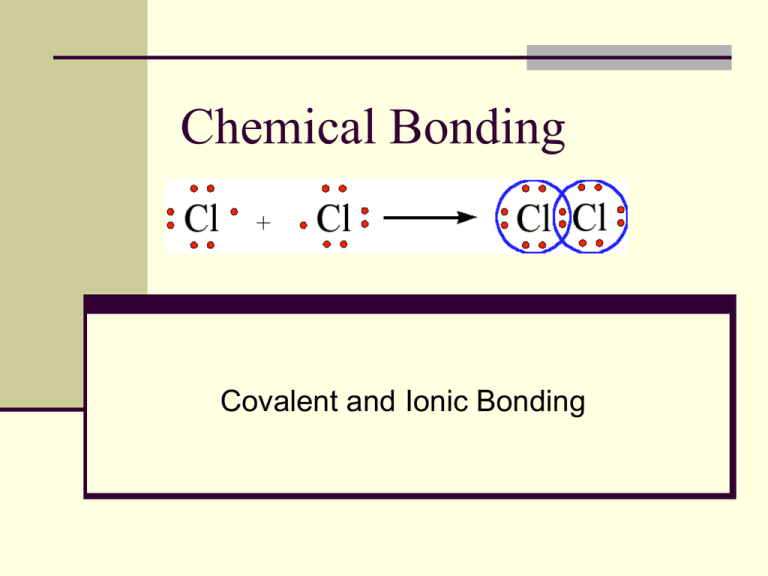
Chemical Bonding Covalent and Ionic Bonding A Chemical Bond A chemical bond is a mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together. Bonds are rarely ever purely ionic or covalent. Electronegativity differences between bonding elements determine ionic character. 0 0.3 (Nonpolar covalent) 0.3 1.7 (Polar covalent) 1.7 3.3 (Ionic) Examples HCl (3.0 – 2.5) = 0.5, polar – covalent CaCl (3.0 – 1.0) = 2.0, ionic Br-Cl (3.0 – 2.8) = 0.2, nonpolar – covalent Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds A molecular (molecule-atoms held together by covalent bonds) compound is a chemical compound whose simplest units are molecules. The chemical formula of a molecular compound is referred to as a molecular formula. Covalent bonds result in lower potential energies from a balance between attractive and repulsive forces. Bond Length Bond length is the distance between two bonded atoms at their minimum potential energy. Average bond length results from the balance between attraction and repulsion in a stable covalent bond. Bond energy is the energy required to break a chemical bond and form neutral isolated atoms. Bond Length vs. Energy The Octet Rule Chemical compounds tend to form so that each atom, by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons, has an octet of electrons in its highest occupied energy level. Most main-group elements form covalent bonds according to the octet rule. There are some exceptions, for example, Boron that has three valence electrons and tends to bond surrounded by 6 electrons. Electron-Dot Notation and Lewis Structures Electron-dot notation depicts the valence electrons surrounding an atom. Lewis structures utilizes pairs of dots or dashes to represent covalent bonds between atoms. Lewis structure Structural formula Lewis Structures Multiple Bonds Double and triple bonds occur when elements share more than one electron pair. Bonds are generally shorter with higher energy. Ionic Bonding and Compounds Ionic compounds are composed of positive and negative ions that are combined so that the numbers of positive and negative charges are equal. Ions minimize their potential by combining in an orderly pattern known as the crystal lattice. Ionic bonding in NaCl Polyatomic Ions A charged group of covalently bonded atoms is known as a polyatomic ion. SO3-2 CN- NO3- NH4+