Covalent Bonding and Molecules
Covalent Bonding and Molecules
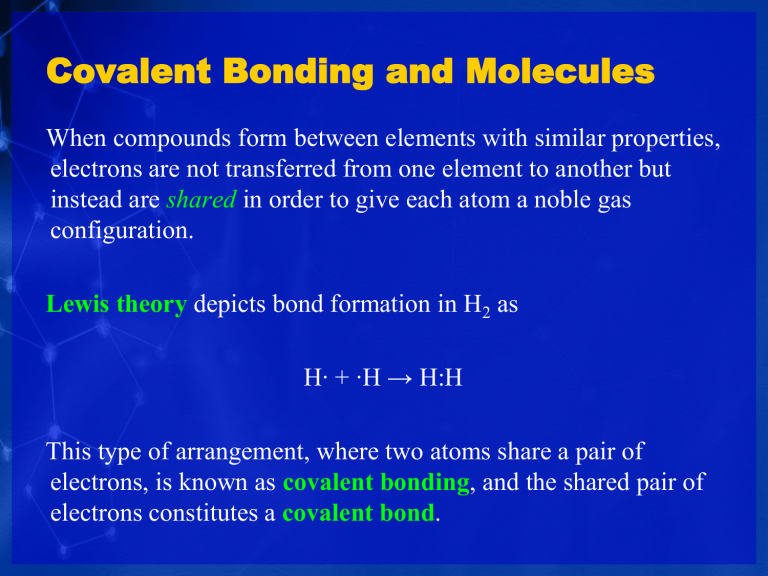
When compounds form between elements with similar properties, electrons are not transferred from one element to another but instead are shared in order to give each atom a noble gas configuration.
Lewis theory depicts bond formation in H
2 as
H∙ + ∙H → H:H
This type of arrangement, where two atoms share a pair of electrons, is known as covalent bonding , and the shared pair of electrons constitutes a covalent bond .
Covalent Bonding and Molecules
Diatomic molecules contain two atoms and may be either heteronuclear or homonuclear .
Polyatomic molecules contain more than two atoms.
Covalent Bonding and Molecules
An empirical formulas , gives the whole-number simplest ratio of elements in a compound.
A molecular formula gives the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule of a compound.
The formulas for ionic compounds are empirical – they can be referred as unit formula or formula unit
Representing Compounds:
Molecular Models
•
Models show the 3-dimensional structure along with all the other information given in the structural formula
•
A structural formula uses lines to represent covalent bonds and shows how atoms in a molecule are connected or b
•
Ball-and-stick models use balls to represent the atoms and sticks to represent the attachments between them
•
Space-filling models use interconnected spheres to show the electron clouds of atoms connecting together
Find the empirical formula for each of the following
The ionic compound that has two aluminum ions for every three oxide ions arabinose, C
5
H
10
O
5
H pyrimidine
H
H
C
C
N
C
N
C
H ethylene glycol
Al
2
O
3
CH
2
O
C
2
H
2
N
CH
3
O
Covalent Bonding and Molecules