authors` original image
advertisement

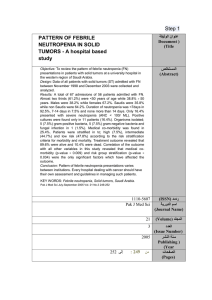
Neutropenia observed on Complete blood count (CBC) Severe if Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) < 0.5 G/l Mild if ANC between 0.5 and 1.5 G/l Frequent etiology: Bacterial infections like strept B, gravidic toxemia and prematurity Rare etiology Maternofetal alloimmunisation - Neutrophil antigens and allo-antibodies Severe combined immunodeficiency immunophenotype lymphocytes Viral fetopathy cytomegalovirus… Congenital neutropenia with early expression Situation 1 New Born Situation 2 Mild neutropenia « Incidental » neutropenia No other blood abnormalities No infection – No recurrent aphthosis No gingivitis No associated pathology Situation 3 Severe neutropenia or mild with severe infection or stomatologic infections or with other blood count anomalies or hepatomegaly/splenomegaly Monthly clinical follow-up for as long as the neutropenia persists (except ethnic) No work up CBC monthly (max) for a year and then according to outcome Emergency consultation if fever Ethnic neutropenia: to be considered if black skin Bone marrow cytology : without delay if other blood anomalies Or organomegaly: malignant hemopathy has to be ruled out Immune deficiency like agammaglobulinemia Immunoglobulin assay (Ig GAM) Lymphocyte immunophenotyping Antibodies against neutrophil membrane antigen Autoimmune neutropenia Initial Work up: no etiology: Clinical and hematological follow up Neutropenia persists or is recurrent Probable congenital neutropenia Recovery from neutropenia : probable post viral neutropenia Bone marrow cytology and cytogenetics Situation 4 Neutropenia in multisystemic disease or dysmorphic syndrome Genetic study depending on context (see table 2)