WHIM Diagnostic criteria
advertisement

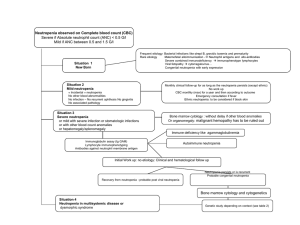
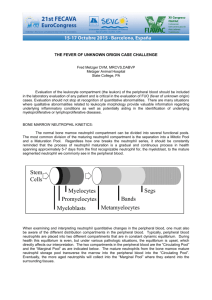
ESID-PAGID Diagnostic criteria for WHIM (Warts-HypogammaglobulinemiaInfections-Myelokathexis) syndrome Definitive diagnosis Male or female patient with chronic neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count of less than 500/L) and myelokathexis (retention of senescent neutrophils in the bone marrow) and one of the following: 1. Mutation in the intracellular C-tail of CXCR4 2. Activating mutation of CXCR4 Probable Diagnosis Male or female patient with chronic neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count of less than 500/L) and myelokathexis (retention of senescent neutrophils in the bone marrow) and two of the following: 1. 2. 3. 4. Chronic or recurrent warts Chronic lymphopenia (absolute lymphocyte count of less than 1500/L) Serum IgG at or below the normal range for age A parent with neutropenia and warts Possible diagnosis Male or female patient with chronic neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count of less than 500/L) and myelokathexis (retention of senescent neutrophils in the bone marrow). Spectrum of Disease WHIM syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder resulting in neutropenia with myelokathexis. Most patients present with recurrent infections at less than 3 years of age. Warts generally begin to appear after five years of age and some patients have hundreds of warts that can include plantar and genital warts. Increased susceptibility to infection from members of the herpes virus family can be seen. Lymphopenia is present in most patients and some patients have very low numbers of B cells. Hypogammaglobulinemia may be present, but the serum immunoglobulin concentrations do not correlate with the number of B cells. Most patients develop a normal neutrophil count during infection.