Primary and Secondary Antibody Deficiency
advertisement

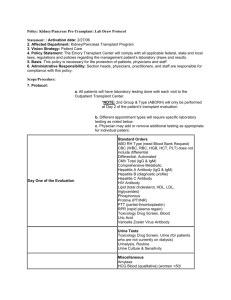
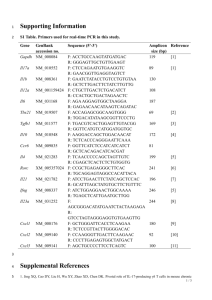
PRIMARY & SECONDARY ANTIBODY DEFICIENCY ANTIBODIES & IMMUNOGLOBULINS PRIMARY ANTIBODY DEFICIENCY The European internet-based patient and research database for primary immunodeficiencies: results 2006-2008. Gathman et al., Clin Exp Immunol (2009); 157 Suppl 1: 3-11. Brit Med J (1989); 298: 516-7 THERAPEUTIC IMMUNOGLOBULIN • 1970s - IMIg • 1980s - IVIg • 1990s - IVIg, SCIg • 2000s - product safety - infusion rates / concentration - immunoglobulin retrieval REPLACEMENT THERAPY TREATMENT OUTCOMES Wood et al. Clin Exp Immunol (2007); 149: 410-423 EFFICACY & ADVERSITY • • • • Immunoglobulin Excipients Soluble CD4/ CD8/ HLA Cytokines Clin Exp Immunol (2004); 136: 111-3 IVIg & SCIg ESID Register 2009 HOME THERAPY 2008 and 2011 SAME OLD SAME OLD • • • • Core of PID management No alternatives Lifelong requirement (usually) Effective (bacterial infection, antibiotic usage, QoL, hospitalisation, life expectancy) • Dose requirement in: - frequent breakthrough infections - chronic inflammation / tissue damage - poor prognosis disease variants WHAT’S NEW? The three Rs: • Reorganisation • Reclassification • Aarrrgh - ongoing uncertainties over dosing / target levels DOSE? Impact of trough IgG on pneumonia incidence in primary immunodeficiency: A meta-analysis of clinical studies. Orange JS et al. Clinical Immunology (2010); 137: 21-30 DOSE: INDIVIDUALISATION ‘The goal of replacement therapy should be to improve clinical outcome and not to reach a particular IgG trough level.’ J Allergy Clin Immunol (2010);125:1354-60 DOSE: INDIVIDUALISATION ‘….individualizing the dosage….is preferable to using mean pharmacokinetic parameters.’ Clin Immunol (2011);139:133-41 RECLASSIFICATION • Specific Antibody Deficiency • Kawasaki Disease ‘Other’ Section REORGANISATION PRIMARY ANTIBODY DEFICIENCY DISORDERS SPECIFIC DISORDERS Thymoma with immunodeficiency (Good’s Syndrome) Combined immunodeficiencies requiring haemopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) Specific antibody deficiency (SAD) Transient hypogammaglobulinaemia of infancy (THI) SPECIFIC DISORDERS DISORDER GOOD’S RECOMMENDATION / REQUIREMENT Profound B cell depletion / significant antibody deficiency HSCT Duration based on B cell reconstitution post-transplantation SAD Robust application of selection criteria THI Define planned duration of therapy prior to initiation (GRADE C, LEVEL III) SUMMARY: PID SECONDARY ANTIBODY DEFICIENCY ANTIBODY DEFICIENCY PRIMARY SECONDARY Malignant disease Drugs Protein-losing states Infection (cause & effect) Systemic disease Iatrogenic causes Chromosomal abnormalities WHAT’S NEW? • Secondary Antibody Deficiency • Revision / collation into a single indication + review outcomes (infection / hospitalisation) + dosing (minimum IgG trough 6 g/L) RECOMMENDATIONS • Irreversible hypo- • Hypo- associated with CLL/NHL/MM etc. and GUIDELINES ‘Systematically developed statements to assist practitioner and patient decisions about appropriate health care for specific clinical circumstances’ • • • • • Evidence-based use Consistency of care Access to safe, high quality products Security of supply Utilising scarce resource OUTCOMES COMPLICATIONS PROGRESSION OF COMPLICATIONS QUALITY OF LIFE WORKING CAPACITY LIFE EXPECTANCY OPTIMISED GROWTH / DEVELOPMENT