Plant Essential Elements
advertisement

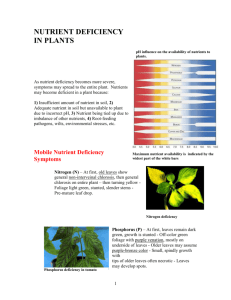
Plants’ Essential Elements Macro and Micronutrients Nutrients • MACRO-required in relatively large amounts • MICRO-required in small amounts, minor or trace elements Macro: non-mineral elements • Carbon (C) • Hydrogen (H) • Oxygen (O) Macro: primary nutrients • Nitrogen (N) • Phosphorus (P) • Potassium (K) Macro: secondary nutrients • Calcium (Ca) • Magnesium (Mg) • Sulfur (S) Micronutrients • • • • • • • Iron (Fe) Copper (Cu) Zinc (Zn) Boron (B) Molybdenum (Mo) Manganese (Mn) Chlorine (Cl) Nitrogen • Promotes growth of leaves and stems • Gives dark green color and improves quality of foliage • Necessary to develop cell proteins and chlorophyll Nitrogen • Deficiency noted when leaves are a sick, yellow-green color • Short stems, small leaves, pale colored leaves and flowers • Slow and dwarfed plant growth Phosphorus • Stimulates early formation and growth of roots • Provides fast and vigorous growth and speeds maturity • Stimulates flowering and seed development Phosphorus • Symptoms of deficiency include slow maturity • Older leaves are a purplish color • Decrease in growth Potassium • Used to form carbohydrates and proteins • Formation and transfer of starches, sugars, and oils • Increases disease resistance, vigor, and hardiness Potassium • Deficiency symptoms include mottled, spotted, streaked or curled leaves • Scorched, burned, dead leaf tips and margins Calcium • Improves plant vigor • Influences intake and synthesis of other plant nutrients • Important part of cell walls Calcium • Symptoms of deficiency include small developing leaves, wrinkled older leaves • Dead stem tips Magnesium • Influences the intake of other essential nutrients • Helps make fats • Assists in translocation of phosphorus and fats Magnesium • Deficiency symptoms include interveinal chlorosis-yellowing of leaves between green veins • Leaf tips curl or cup upward • Slender, weak stems Sulfur • Promotes root growth and vigorous vegetative growth • Essential to protein formation Sulfur • Deficiency symptoms include young leaves are light green with lighter colored veins • Yellow leaves and stunted growth Iron • Essential for chlorophyll production • Helps carry electrons to mix oxygen with other elements Iron • Deficiency symptoms include mottled and interveinal chlorosis in young leaves • Stunted growth and slender, short stems Copper • Helps in the use of iron • Helps respiration Copper • Deficiency symptoms include young leaves are small and permanently wilted • Multiple bud at stem tips Zinc • Helps plant metabolism function • Helps form growth hormones • Aids in reproduction Zinc • Deficiency includes retarded growth between nodes (rosetted) • New leaves are thick and small • Spotted between veins, discolored veins Boron • Affects water absorption by roots • Translocation of sugars Boron • Deficiency symptoms include short, thick stem tips • Young leaves of terminal buds are light green at base • Leaves become twisted and die Manganese • Aids in plant metabolism • Helps in nitrogen transformation Manganese • Deficiency symptoms include interveinal chlorosis • Young leaves die Molybdenum • Aids in plant development • Reproduction Molybdenum • Deficiency symptoms include stunted growth • Yellow leaves, upward curling leaves • Leaf margin burn Chlorine • Essential to some plant processes • Acts in enzyme systems Chlorine • Usually there are more problems with too much chlorine or toxicity than with deficiency Deficiency Assignment • Use the page with the little leaves • Cut out one leaf per nutrient • Color the leaf to match the appearance of deficiency for each nutrient • Past next to the nutrient on your chart