Schizophrenia - Elizabeth
advertisement

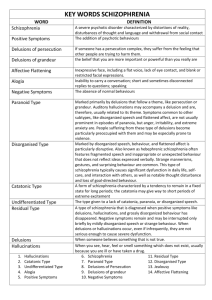
Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a chronic, severe, disabling brain disease that interferes with a person’s ability to think clearly, to distinguish reality from fantasy, to manage emotion, to make decisions, and to relate to others. • Not split-personality disorder • Greek roots describe the fragmented thinking. - “schizo” means split - “prene” means mind • Schizophrenia can be traced back to old Pharaonic Egypt (2nd millennium before Christ). • It was thought to be caused by evil spirits who possessed the bodies of schizophrenics. • Treatment was exorcism. - Innocent methods = playing religious music - Dangerous methods = trephination • 1887 – Dr. Emile Krapelin first identified the disorder as a discrete mental illness called dementia praecox. • Dementia praecox is Latin and means “out of one’s mind for one’s time.” • 1911 - The word schizophrenia was coined by a Swiss psychiatrist named Eugen Bleuler. Positive Symptoms 1. “Positive” – extra, beyond what normal people experience Hallucinations Hearing voices that are not really there (most common) Seeing people or objects that are not really there Smelling scents that do not really exist Thinking he/she is being touched Delusions Delusions of persecution – believe people are trying to harm him/her Delusions of reference – believe TV characters or books are specifically talking to him/her Delusions of influence – believe he/she are being controlled by external forces like aliens or demons Thought disorders Movement disorders Negative Symptoms 2. “Negative” – lacking from what normal people experience Lack of interest Lack of pleasure Flat effect Cognitive Symptoms 3. “Cognitive” Poor ability to understand information and use it to make decisions Trouble focusing or paying attention Problems with “working memory” (the ability to use information immediately after learning Types 1. Paranoid Schizophrenia #1 type of schizophrenia (40%) Characterized by delusions and hallucinations 2. Disorganized Schizophrenia Characterized by very confused speech, social silliness, and neglect of cleanliness 3. Catatonic Schizophrenia Becoming rare Characterized by very disturbed motor behavior Onset and Prevalence • Affects 1 in every 100 people • Men typically develop schizophrenia ages 16-25. • Women typically develop it ages 25-30. Possible Causes • Genes pregnant • Cannabis Use • Infection in womb • Age of Father • Stress during childhood or earlier development • Being born during winter months • Sickness of mother while • Elevated levels of neurotransmitters Paranoia & hallucinations Auditory hallucinations Visual hallucinations Disorganized thoughts Emotional issues Memory & learning problems More Brain • Increased blood flow to some areas • Decreased blood flow to other areas • Extra grey matter lost • Enlarged Ventricles • Reduction in brain tissue Treatments • Americans spend nearly 63 billion a year treating schizophrenia • Antipsychotics “neuroleptic medications” 1. Typical antipsychotics (affect dopamine) 2. Atypical antipsychotics (affect dopamine & serotonin) • Shock Treatments 1. Insulin 2. Electroconvulsive Outlook for Schizophrenics • There are more untreated schizophrenics on the streets than receiving care in hospitals. • 5% of schizophrenics live their lives in hospitals. • 6% are homeless or live in shelters. • 6% live in jails or prisons. • 10% live in nursing homes. • 20% live in supervised homes. • 25% live with a family member. • 28% live independently. • Schizophrenics have a 50x higher risk of attempting suicide than the public. • 40% attempt suicide at least once in their lives. • 10-13% actually kill themselves. • Suicide is the #1 premature cause of death among schizophrenics. Future Treatments • Drugs to lower levels of the STEP enzyme • Drugs to reduce glutamate (a neurotransmitter that excites dopamine release) • Drugs that affect the NMDA receptor (deals with glutamate) • Drugs that affect the mGluR receptors (also deal with glutamate) • Drugs that play a role in the receptors for - Serotonin - Nicotine - GABA • Drugs to slow the loss of gray matter during pruning