ppt

Schizophrenia
Onset can be slow or sudden
Typically exists chronically
Affects ~1% of population
Diagnosis must have at least two symptoms for more that 1 month
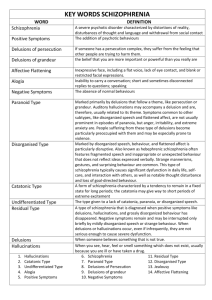
Schizophrenia Symptoms
•Positive Symptoms (abnormal states)
•hallucinations (auditory, visual)
•delusions (grandeur, persecution)
•Negative Symptoms (insufficient functioning)
•avolition (inability to initiate/persist in activities)
•alogia (absence of speech)
•anhedonia (inability to experience pleasure)
•affective flattening (flat emotional response)
•Disorganized Symptoms
•inappropriate affect (laughing/crying at the wrong times)
•disorganized speech (illogical, rambling, tangential)
•disorganized behavior (catatonia, agitation/immobility)
Schizophrenia Subtypes
•Paranoid Type
•hallucinations
•delusions
•Catatonic Type
•unusual motor responses
•remaining in a fixed position
•excessive activity or rigidity
•echoing words or movements of others
•Disorganized Type
•speech problems
•behavior problems
•flat or inappropriate affect
Schizophrenia and Gender
Schizophreni
Genetic Risk by Relatedness
•
The Evidence:
•Family History
•Twin Studies
•monozygotic (50%)
•same handed (92%)
•dizygotic (15%)
•both are carriers
•Adopted Children
•more like bioparents
•
Single Gene?
•Probably not
Brain Structure Abnormalities
Increased Lateral Ventricles
Normal
Brain Structure Abnormalities
Reduced Hippocampus and Amygdala
Affected
Affected
Normal
Brain Structure Abnormalities
Hippocampal Pyramidal Cell Disorganization
Brain Structure Abnormalities
Atypical Frontal Lobe Functioning
• Evidence:
•smaller forebrain
•smaller cerebral cortex
•smaller dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
•fewer cortical neurons
•smaller cortical neurons
•abnormal neuronal development
•neurons remain in white matter
•fail to arrange in neat order
•abnormal CAMs
•less metabolic activity
•hypofrontality
•failure to increase activity following task
•abnormal EEGs
Neurobehavioral Hypothesis
• Maternal/Fetal Evidence:
•extensive maternal bleeding
•prolonged labor
•delivery complications
•low birth weight
•low head circumference
•body length:body weight
•multiparity
•
Anectodal Evidence
•Dutch births during WWII
•Season of birth effect
•higher for winter pregnancies
•parallel with virus exposure
Dopamine Hypothesis of
Schizophrenia
Abnormal levels of Dopamine lead to the schizophrenic symptoms
•
1. Amphetamine Psychosis
•Chronic users develop schizophrenic symptoms
•paranoia, delusions of persecution, auditory hallucinations
•Amphetamine exacerbates schizophrenic symptoms
•Amphetamines promote the release of catelcholamines
•particularly dopamine
• 2. Antipsychotic Drugs
•chlorapromazine is a dopamine antagonist and antipsychotic
•block specifically D2 and D4 receptors in the limbic system
•effectiveness is related to magnitude of blockade
• 3. Parkinson’s Disease
•some patients receiving L-dopa become psychotic
•some schizophrenic patients on antipsychotics develop Parkinson’s symptoms