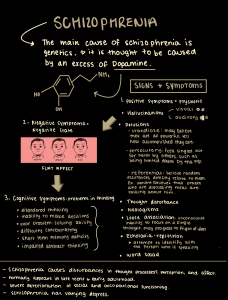
What is Schizophrenia? a brain disease that is diagnosed in late adolescence or early adulthood •Schizophrenia is a primary psychotic disorder. •Symptoms affect the mind by enabling loss of contact with reality •Psychotic disorders can cause abnormalities different symptomatic domains such as delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thoughts, and abnormal motor behavior Signs and symptoms Positive symptoms: Hallucinations, illusions, disorganized speech, paranoia, bizarre behavior Negative Symptoms: apathy, withdrawal, affect, anhedonia, anergia Cognitive symptoms: impairment of insight, problems with working memory, inability to sustain attention RISK FACTORS Environment: drug use, Social adversity, chronic poverty, and growing up in high crime areas or in a foreign culture Genetic Alterations of brain structure: excess levels of dopamine Non-pharmacological treatment hospitalization ( Acute phase to ensure safety, medical workup, testing) Strategize safety & symptom stabilization Patient & family education Skills training (psychosocial) Relapse prevention skills Social/ vocational/ coping skills improvement Pharmacological treatment Antipsychotic Medications: Alleviate the symptoms of schizophrenia, no cure - Psychotic symptoms return with medication noncompliance - Some clients can relapse psychosis even with medication compliance -Acute exacerbations of schizophrenia, reduces the number of relapses -Typical 1ST generation: has intolerable side effects -Atypical 2nd generation : less side effects Typical antipsychotics -target positive symptoms of schizophrenia Examples of typical antipsychotics: -chlorpromazine -fluphenazine -haloperidol -perphenazine -Inexpensive Available in oral and IM injection forms - both immediate and long-acting injections (LAIs) Significant risk of side effects and potential adverse effects such as Extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) , Akathisia, Acute dystonia , Pseudoparkinsonism, Tardive dyskinesia (TD) ,Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS), Agranulocytosis, body temperature alterations, Photosensitivity Atypical Antipsychotics Target both positive and negative symptoms Most of them have metabolic syndrome effects such as weight gain •Examples include: •clozapine (Clozaril) : side effects agranulation so patient needs to monitor CBC •olanzapine (Zyprexa): weight gain •paliperidone (Invega) •quetiapine (Seroquel) •risperidone (Risperdal): lactation and Gynecomastia •ziprasidone (Geodon): cardiomyopathy, (seen as prolonged QTc intervals on EKG readings with or without dysrhythmias Reference: Skidmore-Roth, Linda (2021). Mosby's Drug Guide for Nursing Students. (14th ed.). Elsevier. •Varcarolis, E. M., & Fosbre, C. D. (2021). Essentials of psychiatric mental health nursing: A communication approach to evidence-based care (4th ed.). Elsevier.