Section 7: Common Disorders in Adults Seasonal Affective Disorder
advertisement

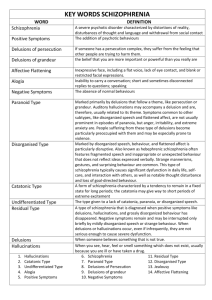
Section 7: Common Disorders in Adults Seasonal Affective Disorder • Depression that occurs at the same time every year • Can cause – Substance abuse – Suicidal thoughts / behavior – School / work problems – Social withdrawal Symptoms • • • • • • • Depression Anxiety Loss of energy Oversleeping Appetite changes Weight gain Loss of interest Why? • Biological clock • Living further from equator • Family history • History of depression / bipolar disorder Treatment • • • • Light Therapy Antidepressants Psychotherapy Home remedies – Exercise – Brighten rooms – Get outdoors Postpartum Depression • Most mothers get baby blues for a brief time – Trouble sleeping – Mood swings • Postpartum depression is more intense and longer lasting • Men just as likely to develop Symptoms • • • • • • • • Loss of appetite Insomnia Intense irritability and anger Feelings of shame / guilt Severe mood swings Difficulty bonding with baby Fatigue Thoughts of harming self / baby Why? • Physical changes • Emotional factors • Lifestyle influences Treatment • Antidepressants • Home remedies – Realistic expectations – Make time for self – Avoid isolation – Healthy lifestyle Section 8: Schizophrenia Schizophrenia • Most serious mental disorder • Hallucinations (usually auditory), delusions, thought disorders • Social withdrawal, loss of social skills, loss of normal emotional responsiveness • Distortion/disturbance of cognition, emotions, perception, and motor functions Example of delusional thoughts • “This morning when I was at Hillside (Hospital), I was making a movie. I was surrounded by movie stars…I’m Mary Poppins. Is this room painted blue to make me upset? My grandmother died four weeks after my eighteenth birthday.” Slide # 12 Early Warning Signs • Mother’s long-lasting schizophrenia • Birth complications, oxygen deprivation, low birth weight • Short attention span & poor muscle coordination • Disruptive and withdrawn behavior • Emotional unpredictability • Poor peer relations and solo play Slide # 13 Some more on Schizophrenia • Loss of contact with reality • Lives life in an unreal dream world • No single cause or cure • Collection of symptoms Slide # 14 Symptoms of Schizophrenia • • • • Delusions/paranoia Hallucinations Language changes Positive / negative symptoms • Movement changes • Diverted attention Slide # 15 Types of Schizophrenia • Paranoid • Catatonic • Disorganized / Undifferentiated • Residual http://imgur.com/a/15A60 Paranoid Schizophrenia • Complex delusions • Perceived persecution • Hallucinations of smell, taste, other bodily sensations • Unseen voices that give them commands • Belief that they have a special mission Slide # 17 Paranoid Schizophrenia • Delusions or frequent auditory hallucinations; all relating to a single theme • Have less disordered thoughts & bizarre behavior than other types • Agitated, confused, afraid Catatonic Schizophrenia • Catatonic state: mute, immobile, mostly unresponsive • “Waxy flexibility” • Unusual postures held for long periods of time Slide # 19 Disorganized / Undifferentiated Schizophrenia • Incoherent language • Inappropriate emotions • Disorganized motor behavior • Hallucinations and delusions Slide # 20 Residual Schizophrenia • Withdrawal • After hallucinations and delusions have disappeared • Coming out of schizophrenia Slide # 21 Causes of Schizophrenia • Brain Abnormalities – Frontal Lobe / cortex / thalamus • Biochemistry – Dopamine • Environment – Pregnancy complications – Family life stress Slide # 22