Psychosis
advertisement

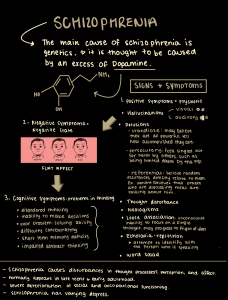
Psychosis First differential: Diagnostic Nosology “Dementia Praecox” vs. “Manic-Depression” (Kraepelin, 1896) – Purely descriptive – no inference – in the European tradition. Dementia Praecox later termed “Schizophrenia” (Bleuler ,1911) – not purely descriptive – inference-laden Neurodevelopmental – starting very early in life – permanent Neurodegenerative – start any time – worsening over time – fatal “Social Drift” May not have mattered back then --- no effective treatments available yet. Effective treatments are hard to develop w/o accurate diagnosis Later: Thorazine found effective for schizophrenia, Lithium for Bipolar Disorder Sometimes effective treatment aids diagnosis (!) Diagnostic Specifics In the Diagnostic & Statistical Manual (3rd edition on), diagnoses are based on different patterns of signs & symptoms. Common signs of psychosis include Delusions Grandeur Reference Thought Control Thought Insertion/Withdrawal Hallucinations (Typically Auditory, occasionally Visual, othes likely neuropsych) There are no cardinal psychotic sx’s/signs of a single DSM-IV diagnosis. These may be found in Schizophrenia Major Depressive Disorder (“Severe with Psychotic Features”) Bipolar I Disorder (Manic) Delusional Disorder (“Pure Paranoia”) Schizoid & Borderline Personality Disorders (typically transient) Note: Neither delusions nor hallucinations is necessary for the dx of schizophrenia – (sound familiar?) 2 different classes of signs/sx’s Positive(excesses) Delusions Hallucinations Catatonia Disorganized Speech Negative(absence) Avolitional syndrome Poverty of speech (alogia) Apathy Schizophrenia DSM-5: Two changes were made to DSM-IV Criterion A for schizophrenia: 1. the elimination of the special attribution of bizarre delusions and …..auditory hallucinations (e.g., two or more voices conversing). 2. the addition of a requirement …. that the individual must have at least one of these three symptoms: 1. delusions 2. hallucinations 3. disorganized speech. At least one of 3 core “positive symptoms” is necessary for a reliable diagnosis of schizophrenia. Phases: Premorbid -- Prodromal --------Active--------------Residual no signs early signs florid – aftermath - highest suicide risk most intense (compare to Major Dep) DSM dx – duration – 6 months minimum (Active Phase) unless successfully tx’d Prognosis –not based upon dx alone. Characteristics Age of Onset Premorbid Functioning Onset Dominant Sxs Stressors Good Prognosis Later Good Acute Positive Present Poor Prognosis Earlier Bad Insidious Negative Absent