Ecology
advertisement

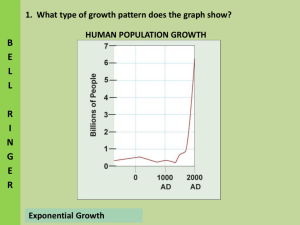
Notes: Human Populations (pg. 10-11) 1. How does the size of the human population change with time? • Increase 2. Why did the population grow slowly for most of human existence? • Life was harsh and there were many limiting factors such as disease. 3. Circle the letter of each reason why the human population began to grow more rapidly about 500 years ago. • • • A. improved sanitation and health care reduced the death rate B. industry made life easier and safer C. the world’s food supply became more reliable. • 4. Why can’t the human population keep growing exponentially forever? – Limited resources • 5. What is demography? – Study of human populations • 6. What factors help predict why the populations of some countries grow faster than others? – Birthrates, death rates, and age structure of a population. • 7. The hypothesis that explains why population growth has slowed dramatically in the US, Japan and much of Europe is called the… – Demographic transition • 8. Throughout much of human history, what have been the levels of birthrates and death rates in human societies? – High death rates and birthrates • 9. What factors lowers the death rate? – Improved sanitation, nutrition and medicine • 10. Is the following sentence true or false? Population growth depends, in part, on how many people of different ages make up a given population? – True • 11. Complete the following flowchart about the demographic transition. • Changes brought about by modernization lower the death rate Births greatly exceed deaths, resulting in rapid population increase as modernization continues, the birthrate decreases and population growth slows the birthrate falls to meet the death rate, and population growth stops • 12. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about human population growth. – B. the worldwide human population is still growing exponentially – C. most people live in countries that have not yet completed the demographic transition – D. the demographic transition has happened in the United States • 13. What do age-structure diagrams graph? – Number of people in different age groups within a population • 14. What do age structures of the US and Rwanda predict about the population growth of each country? – US is showing slow and stable growth while Rwanda’s population should double in 30 years. • 15. By 2050, the world’s population may reach how many people? – 9,078,850,714 • 16. What may cause the growth rate of the world population to level off or even slow down? – Countries growing exponentially will move toward demographic transition • 17. What do many ecologists suggest will happen if the growth in human populations does not slow down? – There will be serious damage to the environment and global economy. Pg. 12 Human Population Review • 1. The human population size has increased over time. • 2. Birthrates, death rates and age structure population are factors that help predict population growth rates. • 3. Describe the birth and death rates of this population. – High birthrate and death rate. • 4. Has this population undergone the demographic transition? Explain. – No because they are still growing rapidly. (Many young people) 5. The approximate human population of Earth in the year 2000 was: 500,000,000 6. Agriculture began in about: 8500 BC 7. The most rapid increase in population was caused by the: Industrial Revolution 8. In the past 5000 years, the event that temporarily halted population increase was: Bubonic Plague 9. The steepest climb in population occurred approximately between the years ______________ and the present. 1500 AD